Integrating BigQuery and Snowflake can significantly enhance data operations within any organization. This blog will guide you on the best methods to connect BigQuery to Snowflake, explaining the advantages and giving detailed, step-by-step tutorials on using Coefficient, Hevo Data, and Airbyte.
Advantages of Connecting BigQuery to Snowflake
- Simplify data architecture: Consolidate your data warehousing and analytics tools by moving data from BigQuery to Snowflake
- Enhance data security: Take advantage of Snowflake’s advanced security features to better protect your sensitive data
- Improve query performance: Leverage Snowflake’s optimized query processing to analyze large datasets more efficiently
Connecting BigQuery and Snowflake: 3 Methods
Connecting BigQuery and Snowflake is crucial for businesses looking to consolidate their data and gain valuable insights. With a range of solutions catering to different needs and user profiles, organizations can choose the best approach to streamline their data integration process.
|
Solution |
Best For |
|
Coefficient |
Data analysts and business users who need to combine BigQuery and Snowflake data for ad-hoc analysis and reporting using a no-code spreadsheet connector. |
|
Fivetran |
Companies that require continuous replication of large volumes of data from BigQuery to Snowflake, ensuring data consistency and enabling near real-time analytics. |
|
Stitch |
Organizations seeking an easy-to-use, affordable solution for moving data from BigQuery to Snowflake, with pre-built connectors and a straightforward interface for configuring data replication jobs. |
How to Connect BigQuery to Snowflake
Method 1: Coefficient – No-Code and User-Friendly
Coefficient connects your spreadsheet to all your business data without a single line of code. It provides a user-friendly interface and automatic data updates, making it a reliable option for both technical and non-technical users.
Relevant Features:
- No-code 2-way sync functionality
- Automatic data updates
- Affordable pricing plans
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Simple, no-code setup
- Automatic data updates
- Affordable pricing plans
Cons:
- Scheduled automations are not included in the free version
Step-by-Step Guide:
Step 1. Install Coefficient
For Google Sheets
Open a new or existing Google Sheet, navigate to the Extensions tab, and select Add-ons > Get add-ons.

In the Google Workspace Marketplace, search for “Coefficient.”

Follow the prompts to grant necessary permissions.

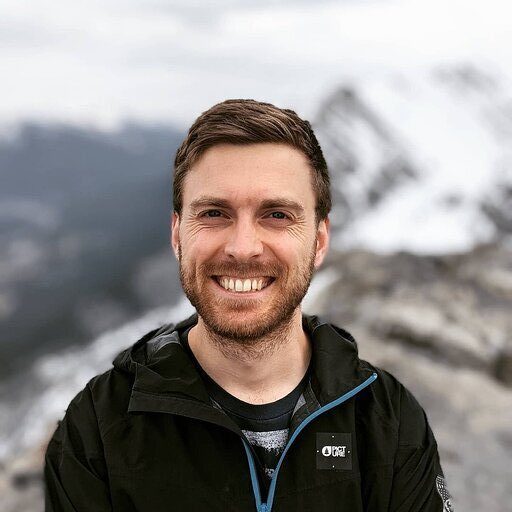
Launch Coefficient from Extensions > Coefficient > Launch.
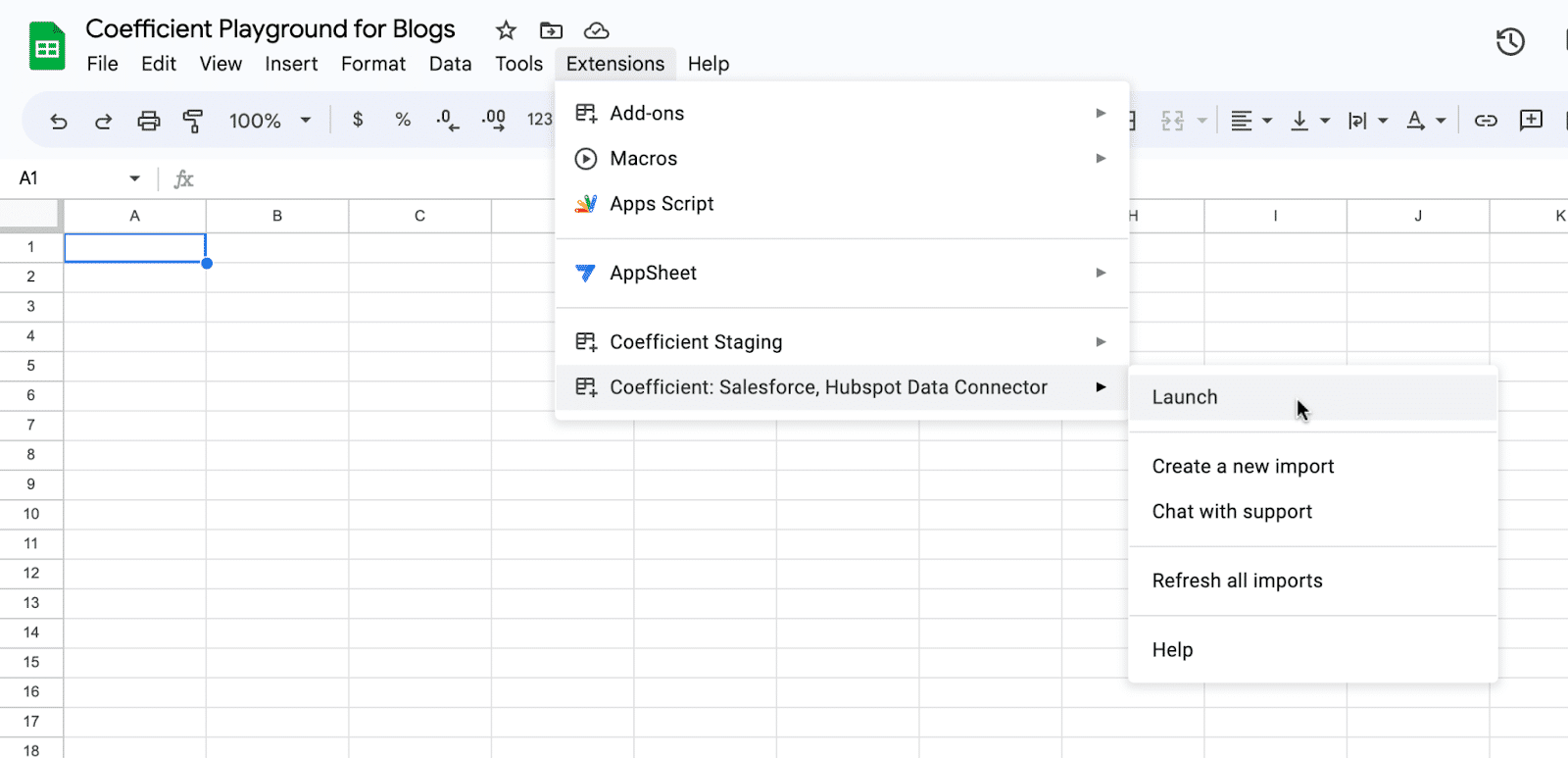
Coefficient will open on the right-hand side of your spreadsheet.

For Microsoft Excel
Open Excel from your desktop or in Office Online. Click ‘File’ > ‘Get Add-ins’ > ‘More Add-Ins.’

Type “Coefficient” in the search bar and click ‘Add.’

Follow the prompts in the pop-up to complete the installation.
Once finished, you will see a “Coefficient” tab in the top navigation bar. Click ‘Open Sidebar’ to launch Coefficient.
Step 2. Import BigQuery Data into Your Spreadsheet
Select ‘Import from…’
Scroll to find and select BigQuery from the dropdown menu.

Step 2. Authorize Connection
If this is your first time linking Coefficient to BigQuery, you’ll need to authorize the connection.
Enter your GCP Project ID.
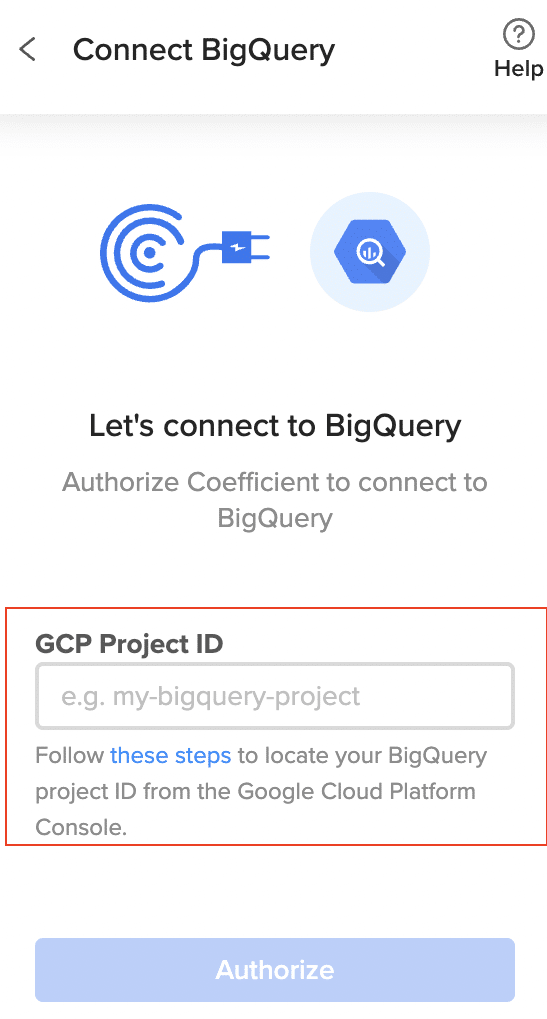
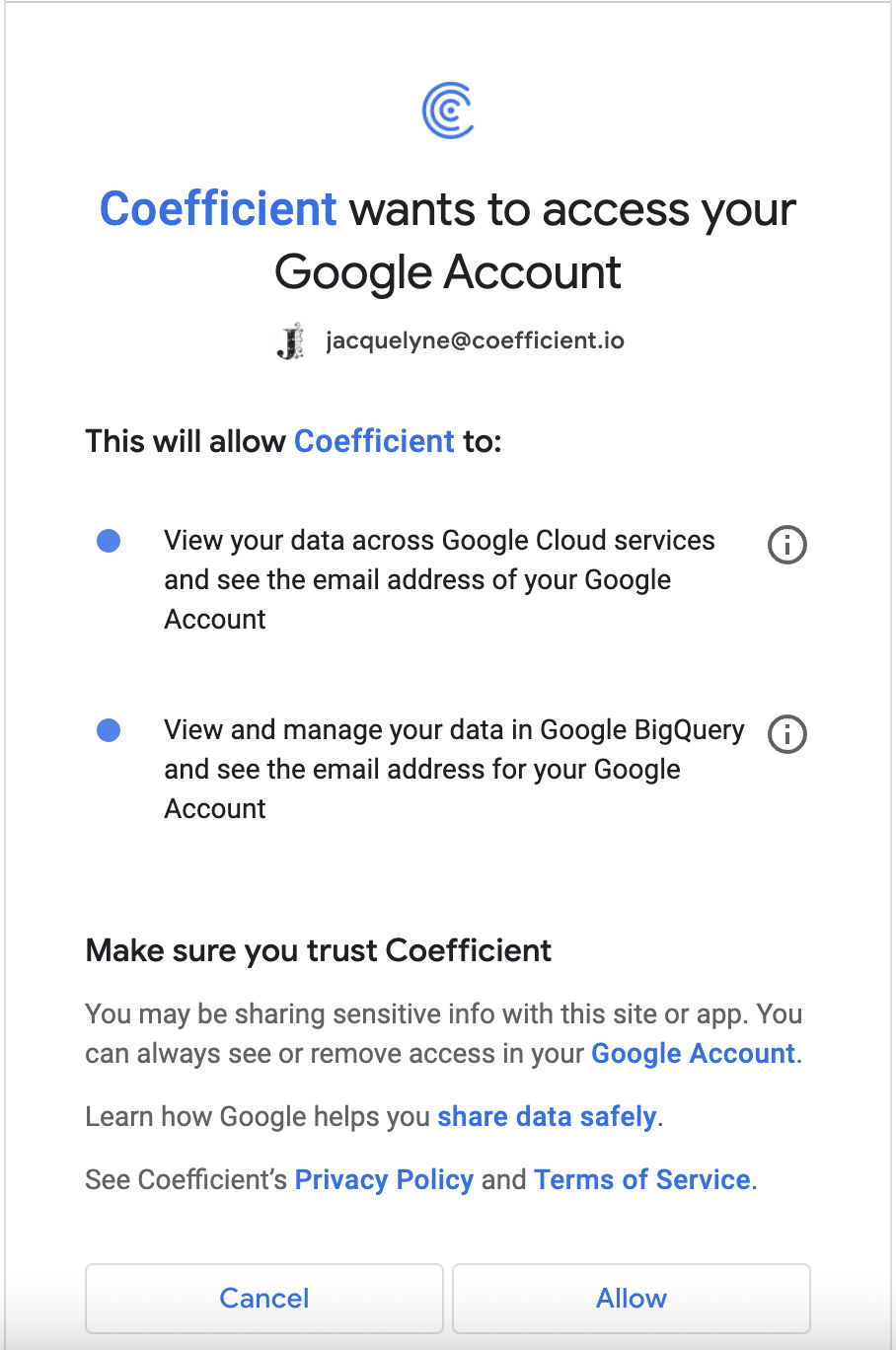
Follow the prompts to grant Coefficient access to your BigQuery data.
As a note: Coefficient is SOC II compliant and makes data security the #1 priority. You can learn more about security here.
Step 3. Setting Up Your Data Import
After authorizing your account, select ‘Import from Tables’ in the Coefficient menu.

The Data Preview window will appear and show all the table schemas from your BigQuery database. Select the table for your import.
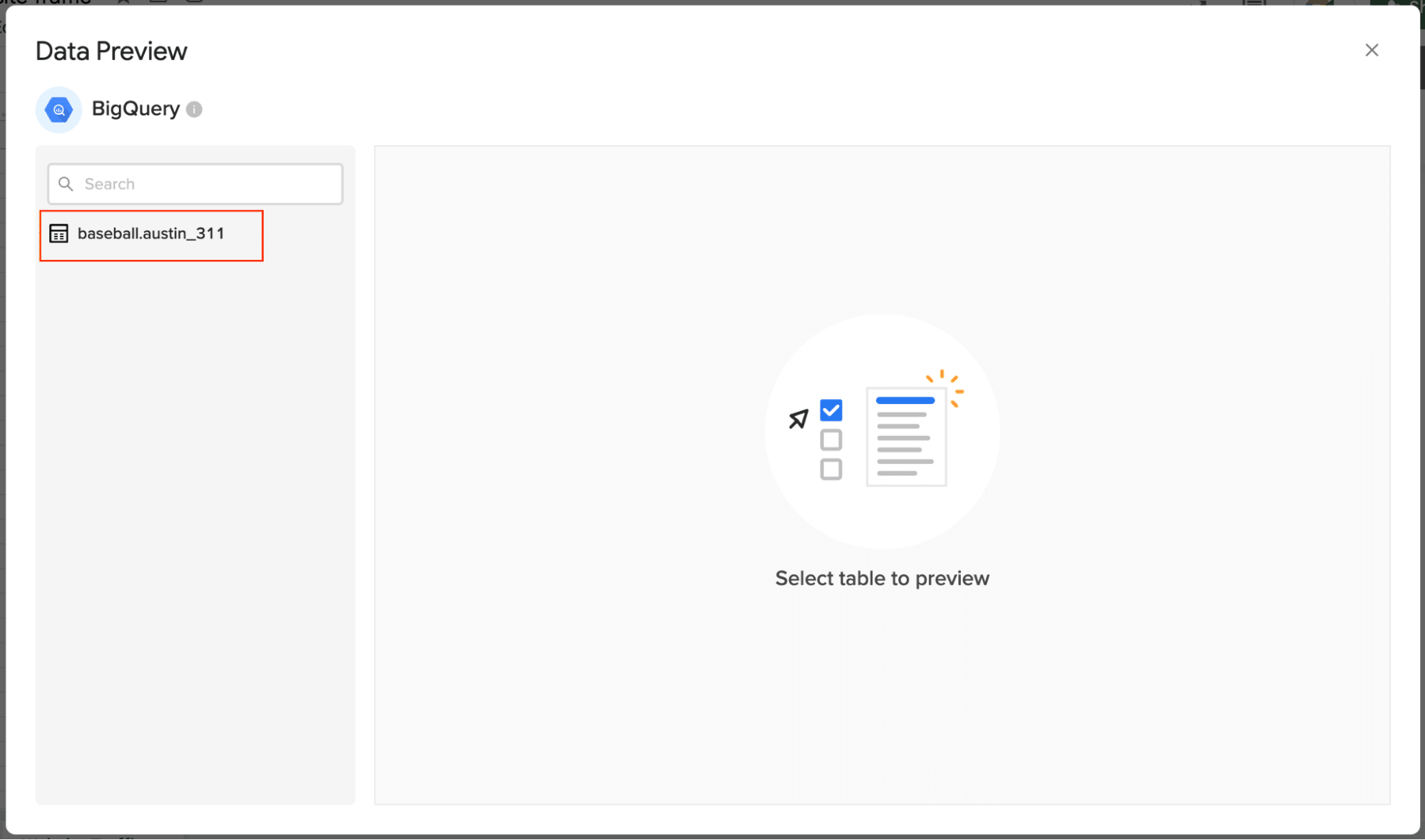
Once the table has been selected, the fields within that table will appear in a list on the left side of the Data Preview window.
Select the fields you need for your import by checking or unchecking the corresponding boxes.

You can further customize your import by adding filters, sorting, or limiting the data import results.

When you’re finished, click the ‘Import’ button.
Your data will populate your spreadsheet in a few seconds!

Step 3. Export Data to Snowflake
Before starting, make sure you’ve connected to Snowflake.
Then, select “Export to…” from the menu.

Choose Snowflake from the list of available data sources.

Select the tab and header rows in your spreadsheet that contains the data you want to export.
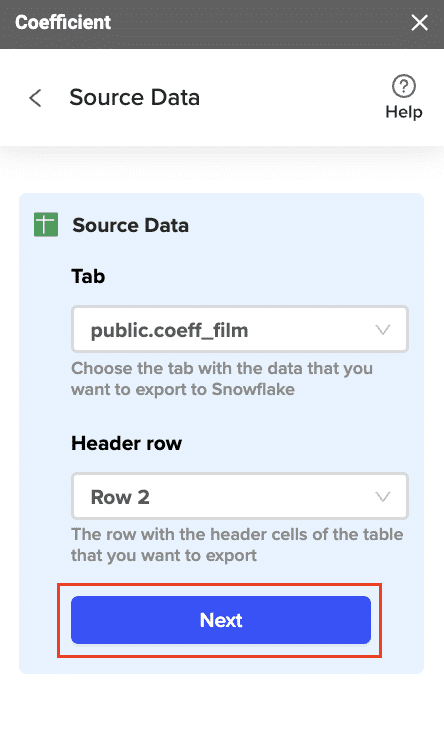
Click “Next” to continue.
Select the table in your Snowflake database that you want to update. Then, select the type of action you want to perform—Update, Insert, Upsert, or Delete.

Map the fields from your spreadsheet to the corresponding Snowflake fields.

Note: Primary Keys (ID fields) are required for Update and Delete actions. For Insert actions, the Primary Key field can be set to auto populate if it’s configured in Snowflake.
(Optional) Specify additional settings such as batch size, whether to export empty cells on an update, and the column for results.
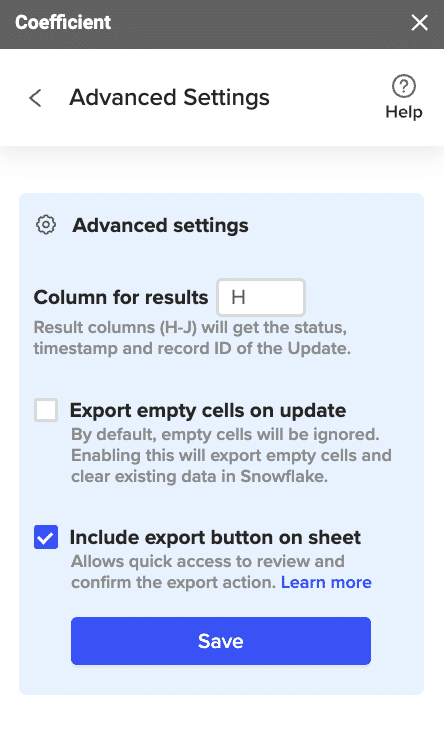
Confirm your settings.

Then, highlight the rows you want to update or export. You can choose to export all rows or specific rows.

After you’re finished, review your settings and click “Export.”
Follow the prompts to confirm your changes.

In a few seconds, data from your spreadsheet will be pushed to Salesforce.
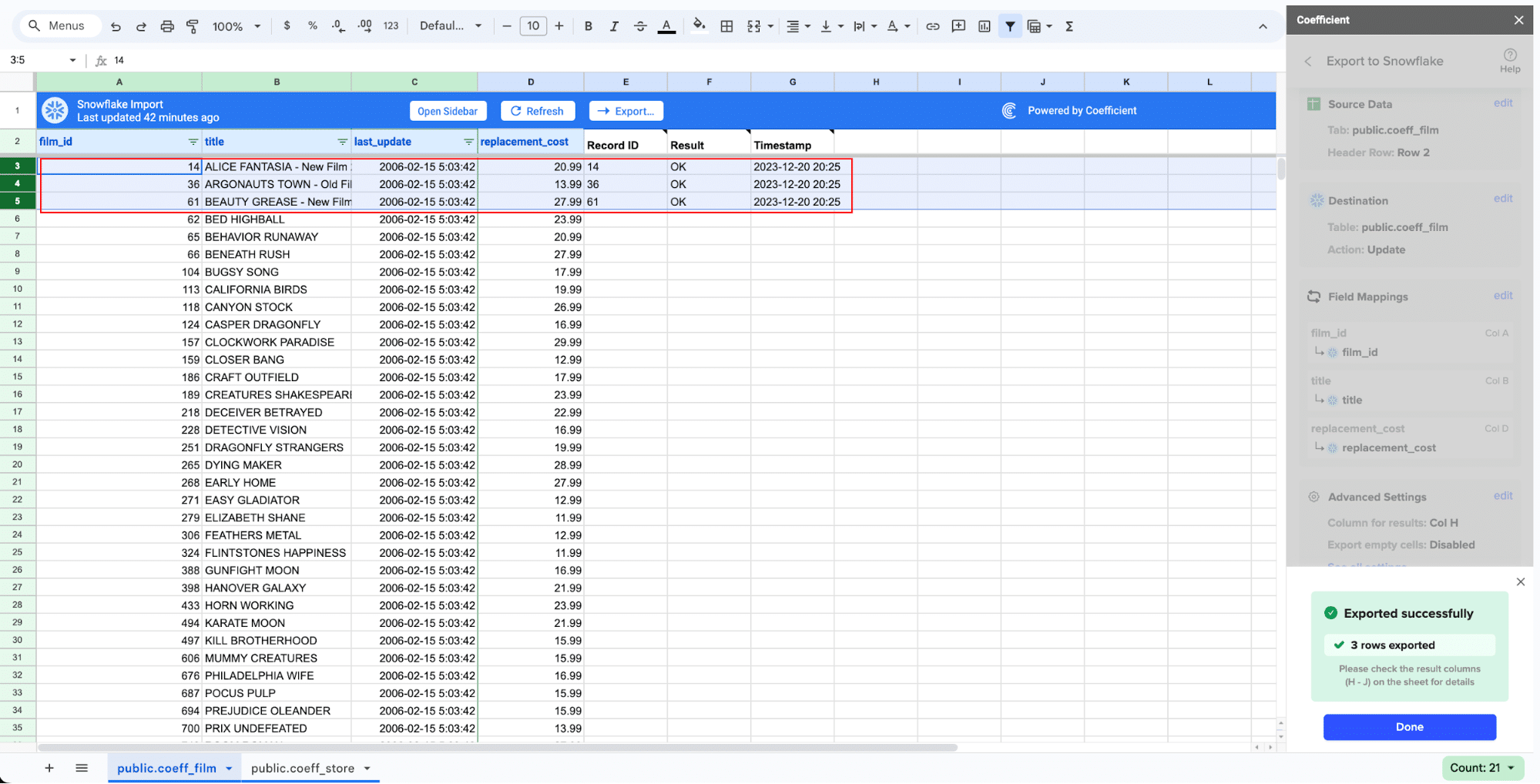
Coefficient will then update the records in Snowflake, displaying the status, record ID, and timestamp of the updates in your spreadsheet.
Method 2: Hevo

Hevo is a powerful no-code platform designed for automated data pipelines.
Relevant Features:
- Automated, real-time data replication
- No-code setup
- Robust monitoring and auto-schema management
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Automated, real-time data replication
- No-code setup
- Robust monitoring and auto-schema management
Cons:
- Advanced features may require a subscription
Step-by-Step Guide:
1. Getting Started with Hevo Data:
- Sign In to Hevo Data:
- Go to the Hevo Data website and sign in or sign up for an account if you don’t have one.
- Create a Pipeline:
- Once logged in, click on the “Create Pipeline” button.
- Select BigQuery as the source from the list of available data sources.
- Configure Source Settings:
- Enter the required credentials for your BigQuery account.
- Provide the necessary details such as the project ID, dataset ID, and other required configurations.
- Test the connection to ensure Hevo can access your BigQuery data.
2. Configuring Snowflake as the Destination:
- Select Snowflake as the Destination:
- After configuring the BigQuery source, proceed to select Snowflake as the destination.
- Enter Snowflake Account Details:
- Provide the necessary Snowflake account details, including the warehouse, database, and schema where you want the data to be loaded.
- Enter the required authentication credentials for Snowflake.
- Set Up Data Mappings:
- Define how the data from BigQuery should map to the corresponding tables and columns in Snowflake.
- Configure any transformations or data processing steps as needed.
3. Executing Data Transfer:
- Enable the Pipeline:
- Once the mappings and configurations are set, enable the pipeline to start the data transfer process.
- Hevo will begin replicating data from BigQuery to Snowflake in real-time.
- Monitor the Data Transfer:
- Use Hevo’s dashboard to monitor the status and performance of the data transfer.
- Check for any errors or issues and make adjustments if necessary.
Method 3: Airbyte
Airbyte is an open-source data integration platform with robust customizable features.
Relevant Features:
- Open-source
- Extensive connector support
- Customizable pipelines
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Open-source
- Extensive connector support
- Customizable pipelines
Cons:
- Initial setup might require technical expertise
- Community-driven support
Step-by-Step Guide:
1. Setting Up Airbyte:
- Download and Install Airbyte:
- Visit the Airbyte website and download the installation package.
- Follow the installation instructions for your operating system to set up Airbyte on your machine.
- Create an Account:
- Once installed, open Airbyte and create an account.
- Log in to the Airbyte dashboard.
2. Configuring Source and Destination:
- Add BigQuery as a Source:
- In the Airbyte dashboard, click on “New Connection” and select BigQuery as the source.
- Provide the necessary credentials and select the dataset you want to sync.
- Configure Snowflake as the Destination:
- Next, select Snowflake as the destination.
- Enter the account details, including the Snowflake warehouse, database, and schema information.
- Authenticate and test the connection to ensure it is properly configured.
3. Running the Data Pipeline:
- Map the Fields:
- Define the mapping between the fields in BigQuery and the corresponding fields in Snowflake.
- Configure any necessary transformations or data processing steps.
- Schedule the Data Sync:
- Set up the synchronization schedule according to your requirements (e.g., hourly, daily).
- Save the configuration and start the sync process.
- Monitor the Pipeline:
- Use Airbyte’s interface to monitor the data pipeline.
- Check logs and status updates to ensure the data is being transferred correctly.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Data Sync Delays:
- Solution: Ensure network stability and check the capacity and resource allocation in Snowflake and BigQuery.
Data Mapping Errors:
- Solution: Double-check field mappings and ensure schema consistency between the source and destination tables.
Authentication Failures:
- Solution: Verify access credentials and permissions for both BigQuery and Snowflake. For Airbyte, ensure the correct service account roles are assigned.
Conclusion
Connecting BigQuery to Snowflake can be done efficiently using the above methods. Each method has unique benefits tailored to various use cases and technical expertise. For a simple and affordable solution, give Coefficient a try today.




