CPM (Cost Per Mille, Cost Per 1000 Impressions) = Total Cost of Campaign / Total Impressions) x 1000
Maximizing Ad Efficiency with the CPM Calculator
In the dynamic landscape of digital advertising, understanding the cost efficiency of your campaigns is critical. Our CPM Calculator is designed to swiftly gauge the cost-effectiveness of your advertising efforts, providing a clear metric to optimize your ad spend and reach.
- Bid farewell to complex calculations; our tool simplifies evaluating your advertising campaigns.
- Effortlessly integrate this calculator into your marketing analysis to consistently monitor performance.
- Customize for precision, ensuring the insights you gain are directly applicable to your campaigns.
Calculation Guide: How to Use Your CPM Calculator
For an accurate CPM calculation, you’ll need:
- The total cost of your advertising campaign.
- The total number of impressions (views) the campaign received.
Roles involved:
- Marketing Analysts to compile and verify cost and impression data.
- Digital Advertising Managers to interpret CPM metrics and adjust strategies.
- Finance Teams to budget and allocate resources effectively.
KPI Overview: The Role of CPM in Advertising
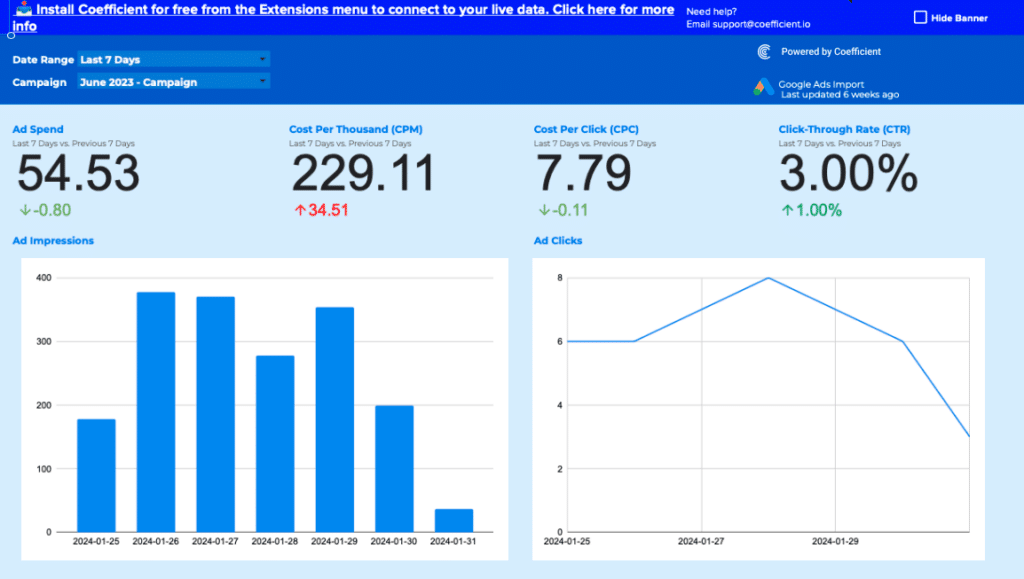
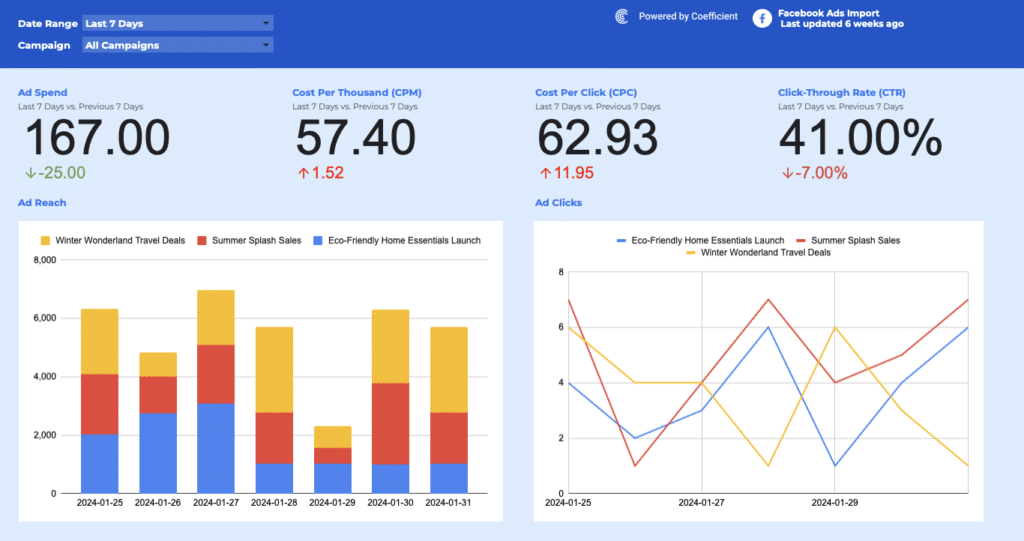
CPM, or Cost per Thousand Impressions, measures how much 1,000 impressions on an advertisement cost. It’s an essential metric for evaluating the financial efficiency of ad campaigns, particularly in the digital space where impressions can number in the millions.
Importance: Why Tracking CPM is Critical
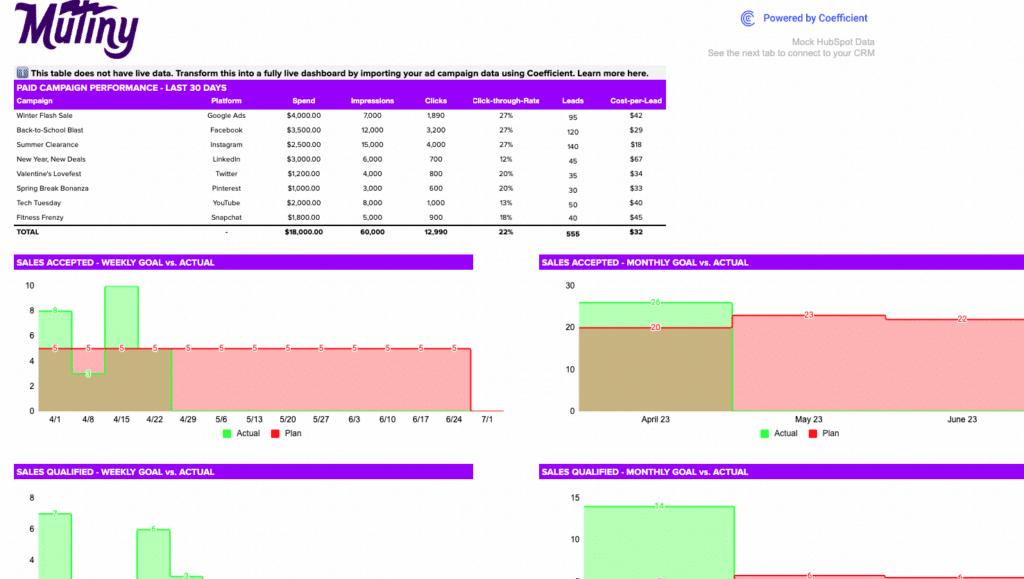
Understanding your CPM allows for the comparison of cost efficiency across different campaigns, platforms, and strategies. It helps in allocating your advertising budget to the most effective channels, maximizing visibility and impact at the lowest possible cost.
Real-world Example: CPM Calculation in Action
Imagine “EcoWear,” an eco-friendly clothing line, spends $2,000 on a digital ad campaign that garners 500,000 impressions. Using the CPM formula, the campaign’s CPM is $4. This means EcoWear spends $4 for every 1,000 impressions its ad receives, offering a benchmark to measure campaign success and guide future ad expenditures.
Improvement Strategies: Lowering Your CPM
- Optimize Ad Creative: Test different ad formats and creative approaches to see which resonates best with your audience.
- Target More Precisely: Use demographic, geographic, and behavioral data to target your ads more effectively.
- Experiment with Ad Platforms: Different platforms may offer more cost-effective impressions.
- Adjust Bidding Strategies: Experiment with bidding strategies to find the most cost-efficient approach for your goals.
- Analyze Peak Times: Allocate more budget to times when your audience is most active, potentially lowering your CPM.
Full Tutorial: Calculating CPM in Excel
- Name two columns: A (Total Cost of Campaign) and B (Total Impressions).
- Enter your campaign data accordingly.
- In a new cell, input the formula: `=(A2/B2)*1000`
- Calculate to reveal your CPM, providing invaluable insight into your campaign’s efficiency.
Drawbacks: The Limitations of CPM
While CPM is invaluable for measuring ad cost efficiency, it doesn’t directly reflect the effectiveness of an ad in driving conversions or sales. It’s important to use CPM alongside other performance metrics for a holistic campaign evaluation.
Usage Contexts: When to Calculate CPM
- Before Launching Campaigns: To set benchmarks and expectations.
- After Campaign Execution: For performance evaluation and future planning.
- During Budget Reviews: To assess and adjust advertising strategies.