Are you looking to connect Amazon Redshift to SQL Server? Whether you need real-time data synchronization or batch transfers, this guide covers three proven methods to establish a reliable connection between Redshift and SQL Server. We’ll provide step-by-step instructions for each approach, helping you choose the best solution for your needs.
Why Connect Redshift to SQL Server?
Before we dive into the methods, let’s explore the advantages of connecting these two powerful database systems:
- Data Warehouse Integration: Combine Redshift’s analytical capabilities with SQL Server’s operational database features for comprehensive business intelligence.
- Cross-Platform Analytics: Enable seamless data flow between cloud and on-premises systems for unified reporting.
- Automated Data Synchronization: Maintain consistent data across platforms for accurate decision-making.
Top 3 Methods to Connect Redshift to SQL Server
Here’s a quick overview of the three methods we’ll cover:
| Solution | Best For |
| Coefficient | Business users who need a no-code solution for real-time data syncing and automated reporting using spreadsheets as an intermediate layer |
| SQL Server Management Studio | Technical users who require direct database connections and native SQL Server tools |
| Airbyte | Organizations needing an open-source solution for batch data transfers with customizable connectors |
Let’s explore each method in detail.
#1 Coefficient: No-Code Solution for Easy Integration

Coefficient provides a spreadsheet-based solution that allows users to connect Redshift to SQL Server without writing code. Using Google Sheets or Excel as an intermediate layer, users can easily transform and validate data before pushing it to SQL Server.
Step-by-Step Guide:
Step 1. Install Coefficient
For Google Sheets
- Open a new or existing Google Sheet, navigate to the Extensions tab, and select Add-ons > Get add-ons.
- In the Google Workspace Marketplace, search for “Coefficient.”
- Follow the prompts to grant necessary permissions.
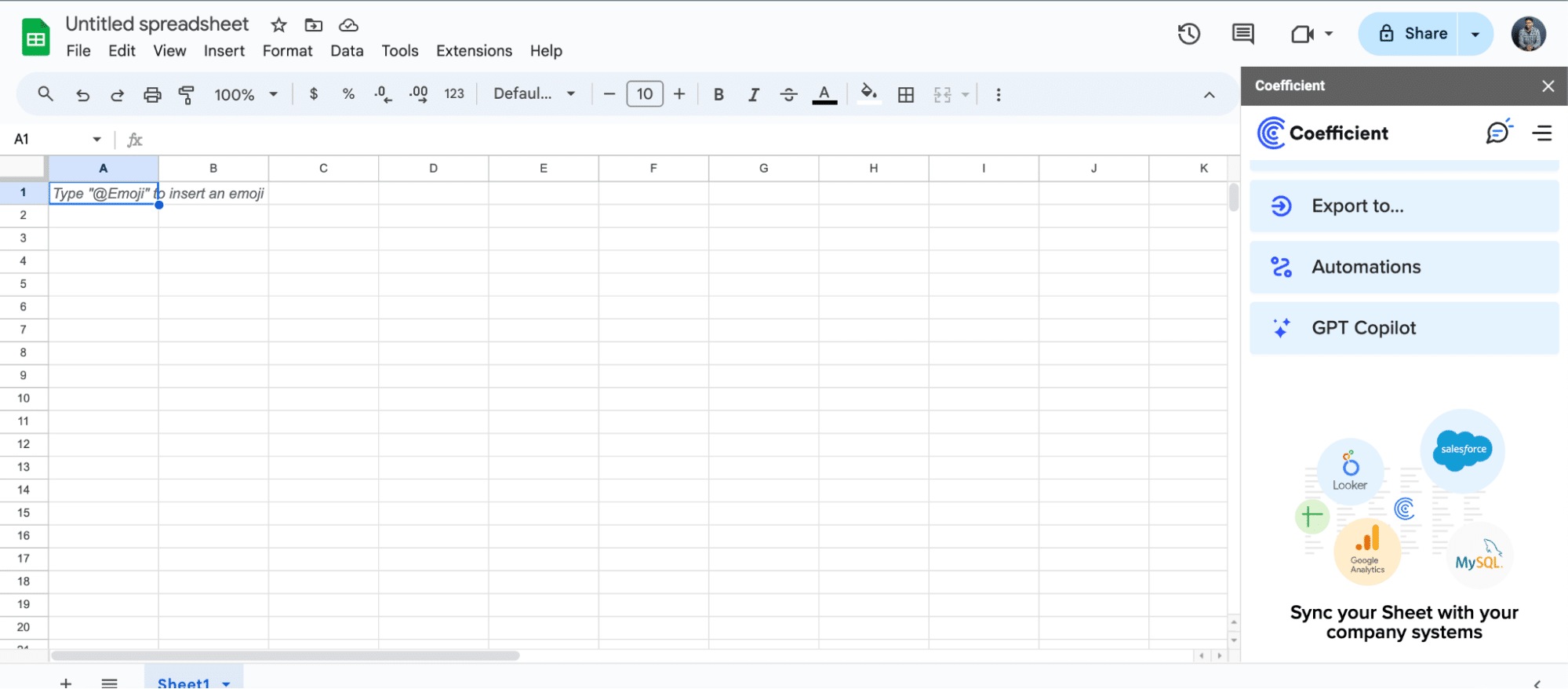
- Launch Coefficient from Extensions > Coefficient > Launch.
- Coefficient will open on the right-hand side of your spreadsheet.
For Microsoft Excel
- Open Excel from your desktop or in Office Online. Click ‘File’ > ‘Get Add-ins’ > ‘More Add-Ins.’
- Type “Coefficient” in the search bar and click ‘Add.’
- Follow the prompts in the pop-up to complete the installation.
- Once finished, you will see a “Coefficient” tab in the top navigation bar. Click ‘Open Sidebar’ to launch Coefficient.

Step 2. Connect and Import Data from Redshift
- Open Coefficient Sidebar: In Google Sheets, go to Extensions > Coefficient > Launch.
- Connect Redshift: Click Import from… and select Redshift.
- Authenticate: Enter Redshift credentials (Host, Database Name, Username, Password, Port) and click Connect.

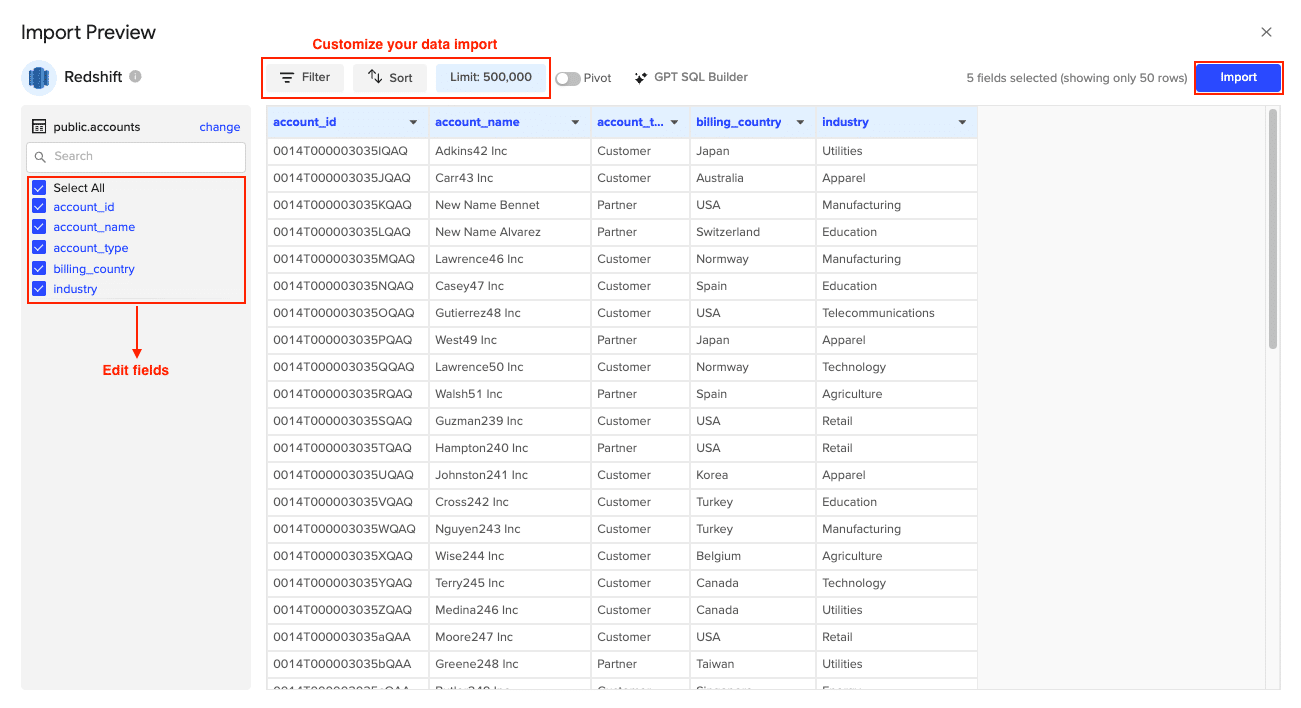
- Select Data: Choose tables/columns or run a custom SQL query. Click Import.
Step 3. Export Data from Your Spreadsheet to MS SQL
Before starting, make sure you’ve connected to MS SQL.
Then, navigate to Coefficient’s menu >Click “Export to…”

Select MS SQL.

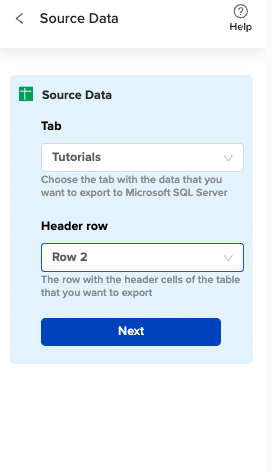
Choose the tab in your workbook that contains the data you want to export and specify the header row that contains the database field headers.
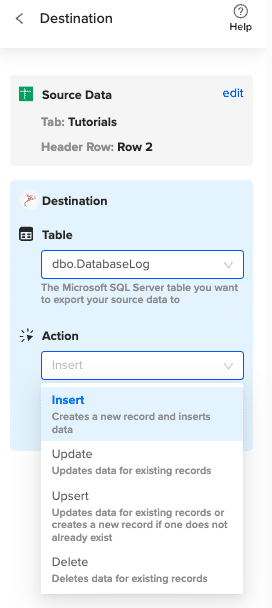
Specify the table in your database where you want to insert the data and choose the appropriate action (Insert, Update, Delete).
Complete the field mappings for the export. Then, confirm your settings and click “Export” to proceed.
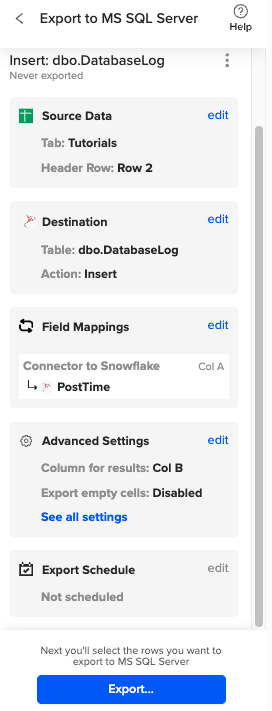
Then, highlight the specific rows in your sheet that you want to export, or choose to export all rows.
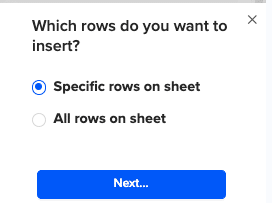
Review your settings and follow the prompts to push your data back to MS SQL.
Pros:
- No coding required
- Real-time data synchronization
- Automated scheduling
- Data validation capabilities
- Spreadsheet-based transformations
Cons:
- Requires spreadsheet as intermediate step
- May not be suitable for very large datasets
For more information on connecting SQL Server to Google Sheets, check out our guide on Microsoft SQL Server to Google Sheets.
If you’re an Excel user, learn how to connect Excel to SQL Server for seamless data integration.
#2 SQL Server Management Studio: Direct Database Connection
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) offers native integration capabilities for connecting to Redshift using linked servers and JDBC/ODBC drivers.
Step-by-Step Guide:
Let’s walk through the complete process of connecting Redshift to SQL Server using SSMS:
- Install the Redshift ODBC Driver First, we’ll set up the necessary driver:
- Download the Amazon Redshift ODBC driver (64-bit) from AWS website
- Run the installer with administrator privileges
- Open Windows ODBC Administrator (64-bit)
Create a new System DSN:
Driver Name: Amazon Redshift (x64)
Data Source Name: RedshiftSource
Server: your-cluster.region.redshift.amazonaws.com
Port: 5439
- Database: your_database
- Test the connection to ensure it’s working
- Configure Linked Server in SSMS Now let’s set up the connection in SQL Server:
— Create the linked server
EXEC sp_addlinkedserver
@server = ‘REDSHIFT_LINK’,
@srvproduct = ‘Amazon Redshift’,
@provider = ‘MSDASQL’,
@datasrc = ‘RedshiftSource’;
— Configure security
EXEC sp_addlinkedsrvlogin
@rmtsrvname = ‘REDSHIFT_LINK’,
@useself = ‘FALSE’,
@locallogin = NULL,
@rmtuser = ‘your_redshift_username’,
@rmtpassword = ‘your_redshift_password’;
- Set up Security and Authentication Configure secure access:
- Create a dedicated SQL Server login for Redshift connections:
CREATE LOGIN redshift_etl
WITH PASSWORD = ‘YourStrongPassword123!’;
CREATE USER redshift_etl FOR LOGIN redshift_etl;
— Grant necessary permissions
GRANT CONNECT ANY DATABASE TO redshift_etl;
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON SCHEMA::dbo TO redshift_etl;
- Create Queries for Data Transfer Set up your transfer queries:
— Create destination table
CREATE TABLE dbo.redshift_data (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
data_value VARCHAR(255),
created_date DATETIME,
last_modified DATETIME
);
— Create transfer procedure
CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.TransferRedshiftData
AS
BEGIN
BEGIN TRY
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
— Clear staging table
TRUNCATE TABLE dbo.redshift_data_staging;
— Copy data from Redshift
INSERT INTO dbo.redshift_data_staging
SELECT *
FROM OPENQUERY(
REDSHIFT_LINK,
‘SELECT id, data_value, created_date, last_modified
FROM source_schema.source_table
WHERE last_modified >= CURRENT_DATE – INTERVAL ”1 day”’
);
— Merge into destination
MERGE dbo.redshift_data AS target
USING dbo.redshift_data_staging AS source
ON target.id = source.id
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET
data_value = source.data_value,
last_modified = source.last_modified
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT (id, data_value, created_date, last_modified)
VALUES (source.id, source.data_value, source.created_date, source.last_modified);
COMMIT TRANSACTION;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION;
THROW;
END CATCH;
END;
- Schedule Automated Jobs Set up SQL Server Agent job:
- Open SQL Server Agent
Create New Job:
— Create job
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_job
@job_name = ‘Redshift_Data_Transfer’;
— Add job step
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobstep
@job_name = ‘Redshift_Data_Transfer’,
@step_name = ‘Transfer Data’,

Stop exporting data manually. Sync data from your business systems into Google Sheets or Excel with Coefficient and set it on a refresh schedule.
Get Started
@subsystem = ‘TSQL’,
@command = ‘EXEC dbo.TransferRedshiftData’;
— Create schedule
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_schedule
@schedule_name = ‘Daily_Transfer’,
@freq_type = 4, — Daily
@freq_interval = 1,
@active_start_time = 010000; — 1:00 AM
— Attach schedule to job
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_attach_schedule
@job_name = ‘Redshift_Data_Transfer’,
@schedule_name = ‘Daily_Transfer’;
— Enable the job
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_update_job
@job_name = ‘Redshift_Data_Transfer’,
- @enabled = 1;
Pros:
- Direct database connection
- Native SQL Server tools
- Advanced query capabilities
Cons:
- Requires technical expertise
- Complex setup process
- Limited automation options
#3 Airbyte: Open-Source Data Integration Platform
Airbyte is an open-source data integration platform that supports connecting Redshift to SQL Server through pre-built connectors.
Step-by-Step Guide:
Let’s set up an Airbyte connection:
- Deploy Airbyte Instance First, let’s get Airbyte running:
- Install Docker on your server
- Pull and run Airbyte using Docker Compose:
# Create directory
mkdir airbyte && cd airbyte
# Download docker-compose file
curl -o docker-compose.yml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/airbytehq/airbyte/master/docker-compose.yml
# Start Airbyte
docker-compose up -d
- Configure Redshift Source Connector Connect to your Redshift instance:
- Open Airbyte UI (typically http://localhost:8000)
- Go to Sources → Add New Source
- Select “Redshift”
Enter connection details:
Host: your-cluster.region.redshift.amazonaws.com
Port: 5439
Database: your_database
User: your_username
Password: your_password
- Schema: public (or your schema)
Add these optional configurations for better performance:
JDBC URL Params:
ssl: true
- sslfactory: com.amazon.redshift.ssl.NonValidatingFactory
- Set up SQL Server Destination Configure where your data will land:
- Go to Destinations → Add New Destination
- Select “Microsoft SQL Server”
Enter connection details:
Host: your-sqlserver.database.windows.net
Port: 1433
Database: your_database
Username: your_username
Password: your_password
- Schema: dbo (or your preferred schema)
Advanced settings:
Batch Size: 10000
- SSL Method: require
- Define Sync Schedule Set up your synchronization:
- Create new connection between source and destination
Choose sync mode:
Sync Mode: Incremental
Cursor Field: last_modified
- Primary Key: id
- Set sync frequency:
- Basic: Every 24 hours at 2 AM
Advanced schedule:
cron: 0 2 * * *
- timezone: UTC
- Monitor Data Transfers Set up monitoring and alerts:
# In airbyte-config/config.yml
logging:
level: INFO
appenders:
– type: file
currentLogFilename: /logs/airbyte.log
archivedLogFilenamePattern: /logs/airbyte-%d.log.gz
archivedFileCount: 7
notifications:
slack_webhook_url: your_webhook_url
email:
smtp_host: smtp.gmail.com
smtp_port: 587
smtp_username: your_email
smtp_password: your_password
from_email: [email protected]
to_email: [email protected]
Pros:
- Open-source solution
- Customizable connectors
- Community support
Cons:
- Requires infrastructure setup
- Limited enterprise features
- Technical maintenance needed
Start Syncing Your Redshift Data to SQL Server Today
Connecting Redshift to SQL Server doesn’t have to be complicated. While each method has its advantages, Coefficient offers the most user-friendly approach with no coding required. Start syncing your data today and experience seamless integration between your Redshift and SQL Server databases.
Ready to get started? Sign up for Coefficient now and transform your data integration process.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Redshift connect to SQL Server?
Yes, Redshift can connect to SQL Server through various methods, including Coefficient’s no-code solution, JDBC/ODBC drivers, or data integration platforms.
How do I transfer data from Redshift to SQL Server?
The easiest way is using Coefficient’s spreadsheet-based solution, which allows you to import Redshift data and push it to SQL Server without coding. Alternatively, you can use SQL Server Management Studio or open-source tools like Airbyte.
How to extract data from Redshift using SQL?
While you can use the UNLOAD command in Redshift, Coefficient simplifies this process by allowing you to extract data through a user-friendly interface and automatically sync it to SQL Server.

