Are you struggling to match and extract specific text patterns in your Google Sheets data? REGEXMATCH is a powerful function that can revolutionize how you handle text-based data.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about using REGEXMATCH in Google Sheets, from basic syntax to advanced techniques.
Step-by-Step Guide: REGEXMATCH
Basic Pattern Matching
Let’s start with some simple pattern matching examples:
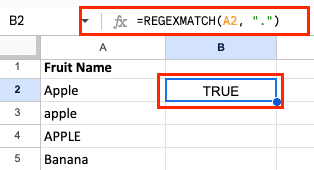
- Match any single character:
=REGEXMATCH(A1, “.”)
This will return TRUE for any non-empty cell.
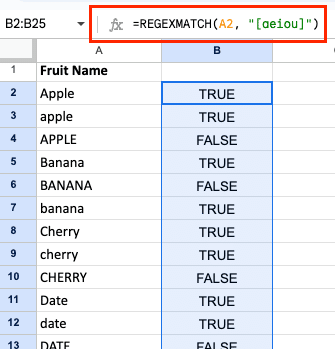
- Match specific characters:
=REGEXMATCH(A1, “[aeiou]”)
This will return TRUE if A1 contains any vowel.
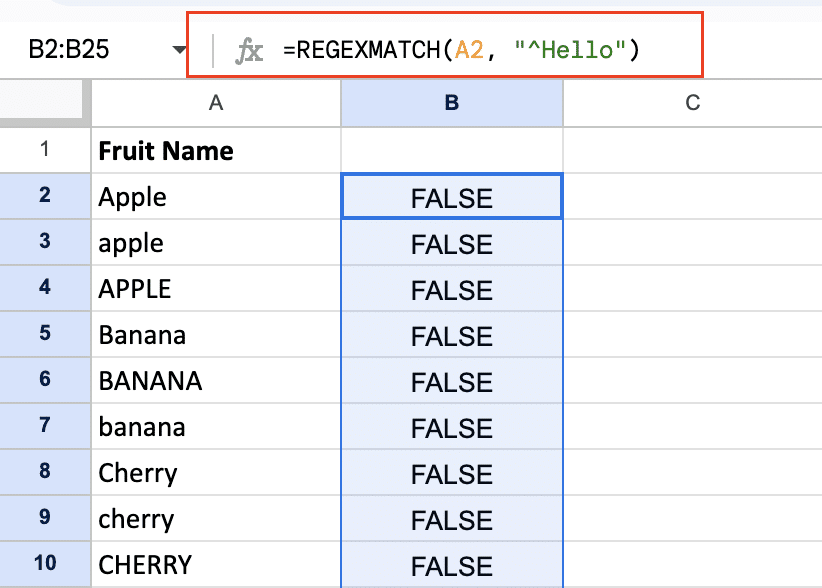
- Match the start of a string:
=REGEXMATCH(A1, “^Hello”)
This will return TRUE if A1 starts with “Hello”.

- Match the end of a string:
=REGEXMATCH(A1, “world$”)
This will return TRUE if A1 ends with “world”.

Case Sensitivity in REGEXMATCH
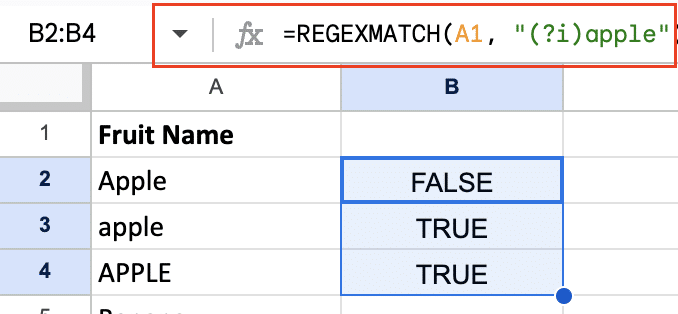
By default, REGEXMATCH is case-sensitive. To make it case-insensitive, use the (?i) flag at the start of your regular expression:
=REGEXMATCH(A1, “(?i)apple”)
This will match “apple”, “Apple”, “APPLE”, or any other case variation.

Advanced REGEXMATCH Techniques
Using Wildcards and Quantifiers
Wildcards and quantifiers allow you to create more flexible patterns:
- *: Matches zero or more occurrences
- +: Matches one or more occurrences
- ?: Matches zero or one occurrence
- {n}: Matches exactly n occurrences
- {n,}: Matches n or more occurrences
- {n,m}: Matches between n and m occurrences
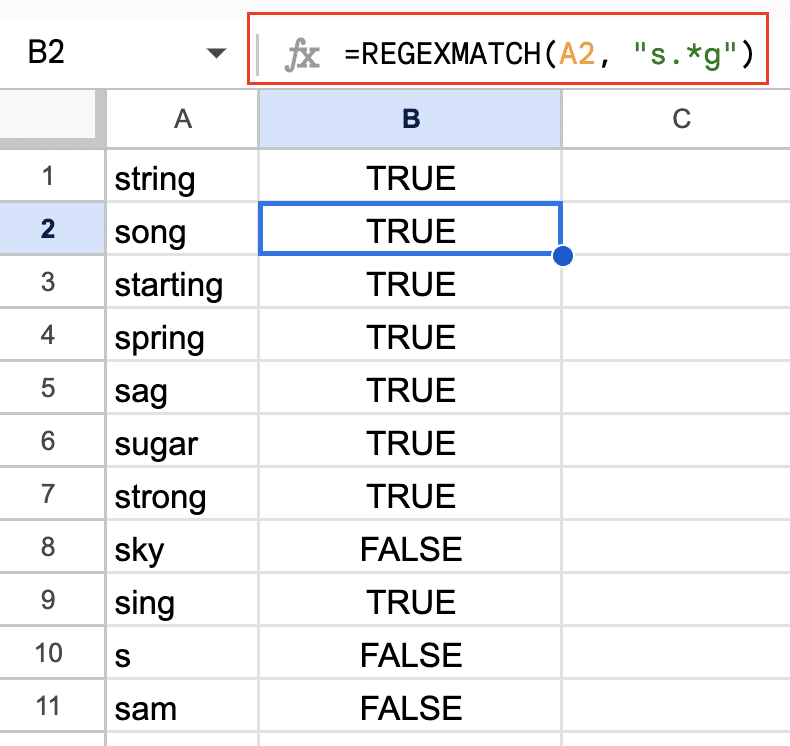
For example, to match a word that starts with “s” and ends with “g”, with any number of characters in between:
=REGEXMATCH(A1, “s.*g”)
Grouping and Alternation
Parentheses () are used for grouping, while the pipe symbol | is used for alternation (OR).
To match either “cat” or “dog”:
=REGEXMATCH(A1, “(cat|dog)”)
To match a repeated pattern:
=REGEXMATCH(A1, “(ha){3}”)

This will match “hahaha”.
Practical Applications of REGEXMATCH
Data Validation and Cleaning
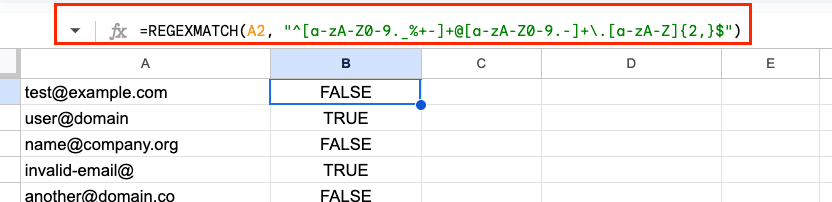
REGEXMATCH is excellent for data validation. For example, to check if a cell contains a valid email address:
=REGEXMATCH(A1, “^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$”)
You can use this in a custom formula for data validation to ensure users enter valid email addresses.
Extracting Specific Information from Text
While REGEXMATCH itself doesn’t extract text, you can use it in combination with other functions. For example, to check if a cell contains a date in the format MM/DD/YYYY:
=REGEXMATCH(TEXT(A1, “MM/DD/YYYY”), “^d{2}/d{2}/d{4}$”)

Stop exporting data manually. Sync data from your business systems into Google Sheets or Excel with Coefficient and set it on a refresh schedule.
Get Started

Combining REGEXMATCH with Other Google Sheets Functions
REGEXMATCH becomes even more powerful when combined with other functions. Here’s an example using ARRAYFORMULA to check multiple cells at once:
=ARRAYFORMULA(REGEXMATCH(A1:A100, “apple”))
This will return an array of TRUE/FALSE values for cells A1 through A100, indicating which cells contain “apple”.
REGEXMATCH vs. Other Regex Functions in Google Sheets
REGEXEXTRACT: When and How to Use It
While REGEXMATCH tells you if a pattern exists, REGEXEXTRACT actually retrieves the matched text. Use REGEXEXTRACT when you need to pull out specific information from a string.
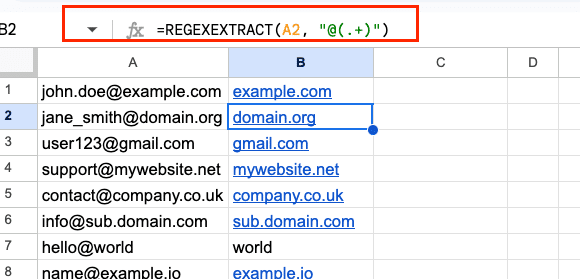
For example, to extract the domain from an email address:
=REGEXEXTRACT(A1, “@(.+)”)
REGEXREPLACE: Modifying Text with Regex
REGEXREPLACE allows you to find and replace text based on patterns. It’s useful for cleaning and standardizing data.
To replace all occurrences of “color” with “colour”:
=REGEXREPLACE(A1, “color”, “colour”)
Choosing the Right Regex Function for Your Needs
- Use REGEXMATCH for yes/no questions about patterns in your data
- Use REGEXEXTRACT when you need to pull out specific information
- Use REGEXREPLACE when you need to modify text based on patterns
Often, you’ll use these functions together. For example, you might use REGEXMATCH to identify cells that need cleaning, then use REGEXREPLACE to perform the cleaning.
Best Practices and Tips for Using REGEXMATCH
Writing Clean and Maintainable Regex Patterns
- Comment your regex: Use (?#comment) syntax to add comments within your regex
- Break complex patterns into smaller, reusable parts
- Use descriptive variable names when storing regex patterns
- Avoid overly complex patterns; sometimes multiple simple patterns are clearer than one complex one
Testing and Refining Your Expressions
- Start with simple patterns and gradually add complexity
- Test your regex on a variety of input data, including edge cases
- Use online regex testers to visualize and debug your patterns
- Keep a library of commonly used patterns for reuse
Mastering REGEXMATCH in Google Sheets
REGEXMATCH in Google Sheets opens up a world of possibilities for data analysis and manipulation. From basic pattern matching to complex data validation, this powerful function can significantly enhance your spreadsheet skills. Remember to start simple, test thoroughly, and gradually build up to more complex patterns. With practice, you’ll be handling even the most challenging text pattern matching tasks with ease.
Ready to take your data analysis to the next level? Discover how Coefficient can supercharge your Google Sheets experience with advanced data integration and automation features. Get started with Coefficient today and unlock the full potential of your spreadsheet data.

