Need to adjust cell ranges dynamically in Google Sheets? OFFSET is your go-to tool. This guide explains how OFFSET creates flexible cell references, making your data analysis both advanced and straightforward.
What Is OFFSET?
OFFSET in Google Sheets shifts a cell range based on your inputs. It is ideal for ever-changing datasets because it alters the range of references as your data grows or shrinks.
Syntax simplified, use OFFSET like this:
- cell_reference: Your starting point.
- offset_rows: Rows to move from the start.
- offset_columns: Columns to shift from the start.
- Height (optional): Range height.
- Width (optional): Range width.
Here are A Few Use Case Examples
Simple OFFSET Example
Objective: To return the sales figure for “Electronics” in “March”.
Click on a blank cell where you want the result to appear.
Enter the formula: =OFFSET(A2,2,1)
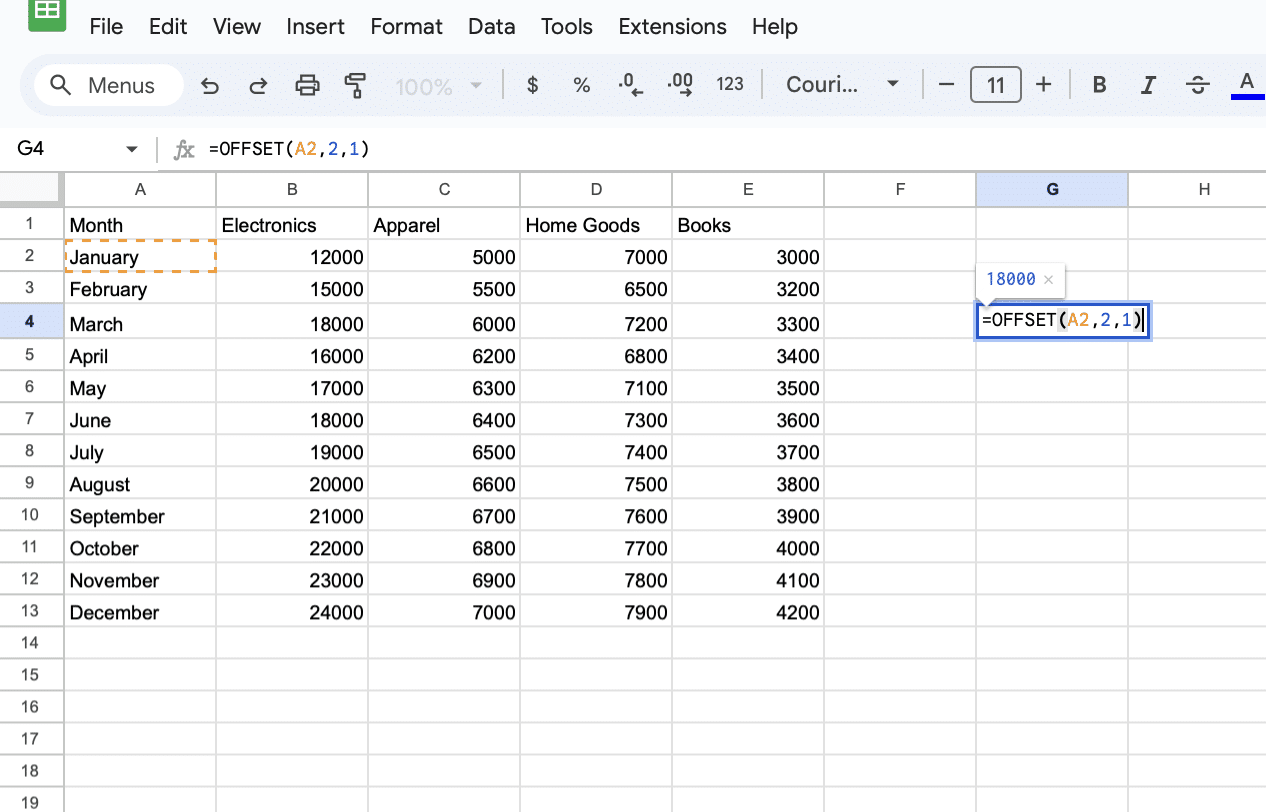
Press Enter. The formula returns “18000”, the sales figure for Electronics in March.
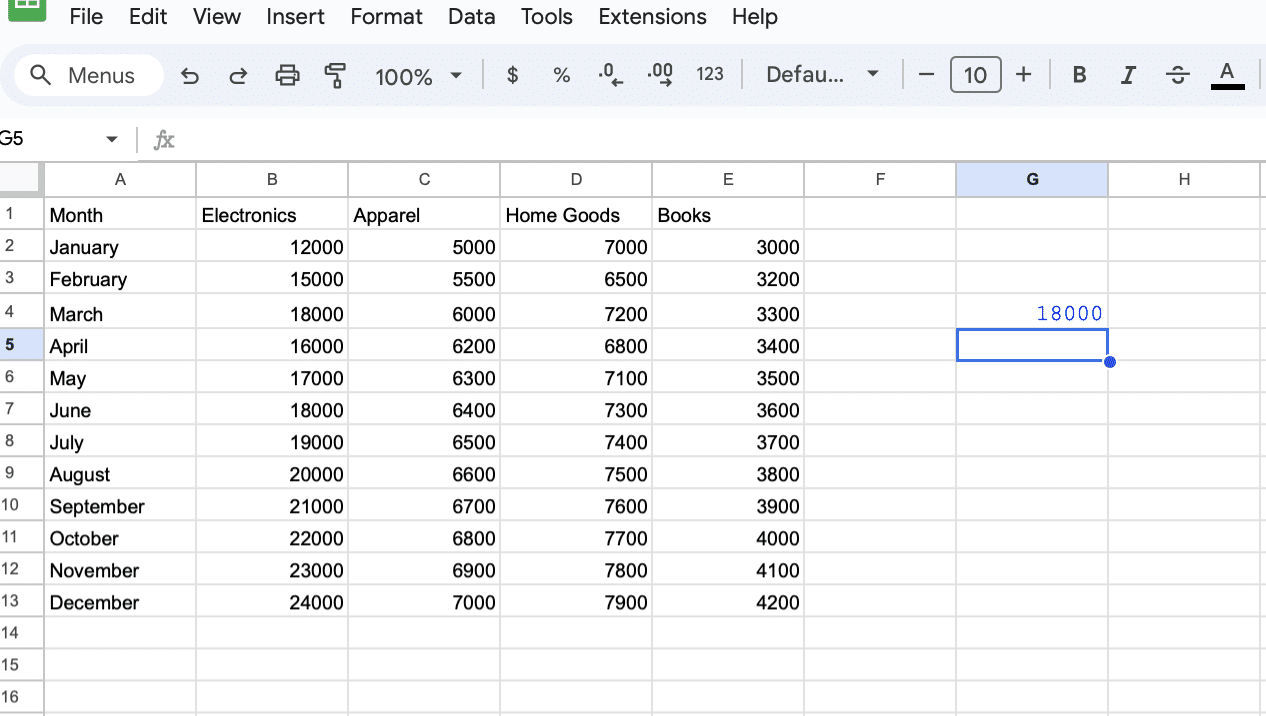
Explanation:
- A2 is the reference cell (January, Electronics).
- We offset two rows down to reach March.
- We offset 1 column right to stay in the Electronics column.
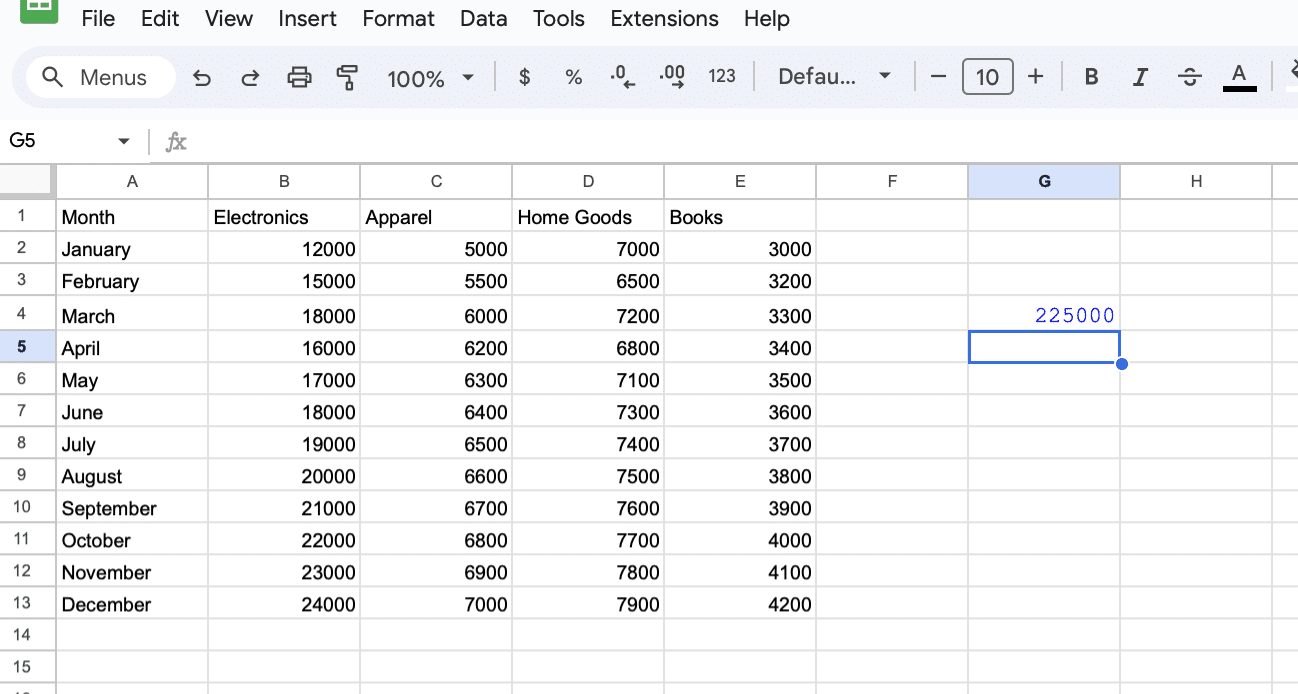
Dynamic Summation of a Column
Objective: Sum the “Electronics” sales figures dynamically, allowing for new months to be added without changing the formula.
In a new cell, enter the formula: =SUM(OFFSET(B2,0,0,COUNTA(B2:B13),1))
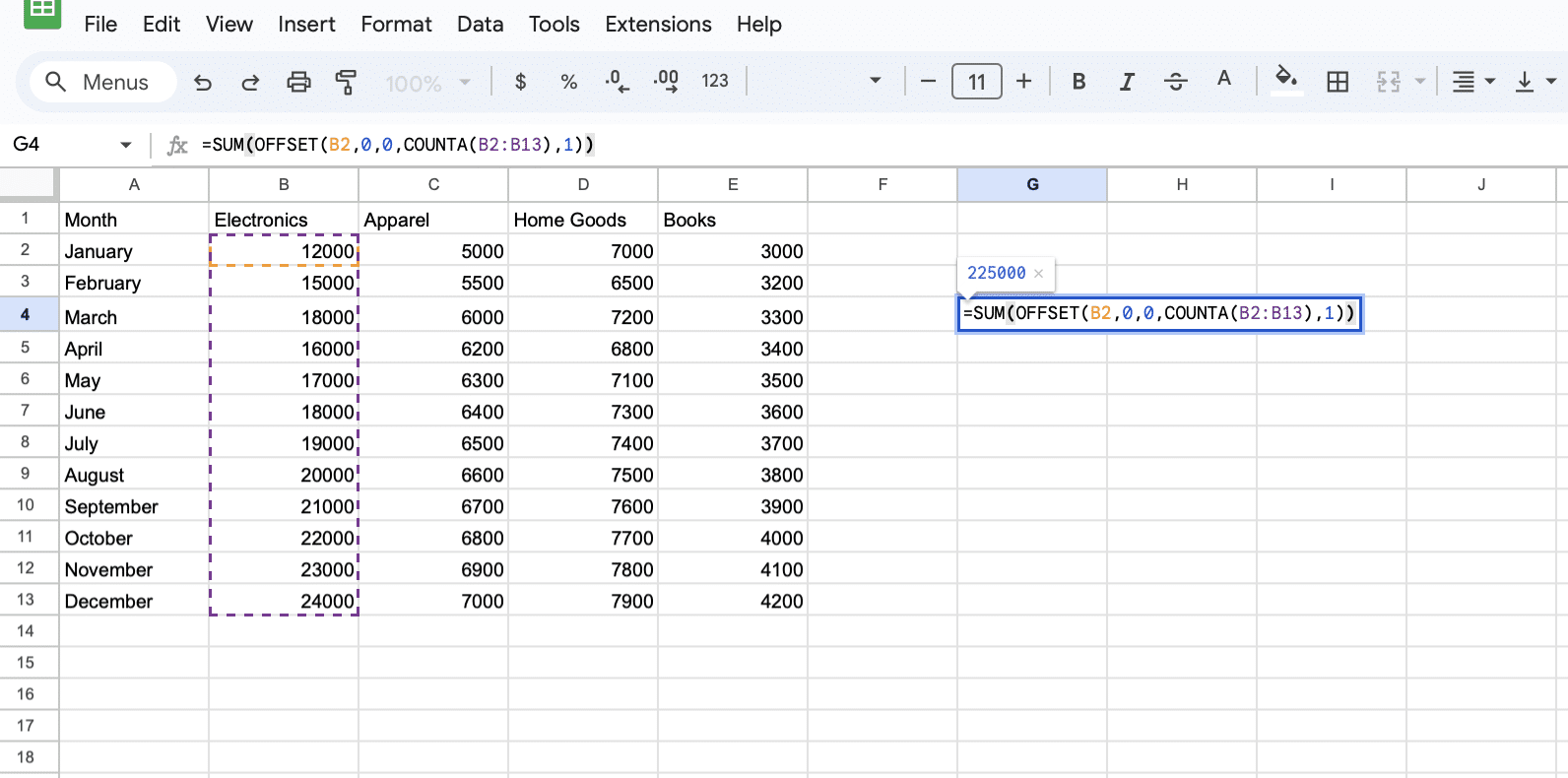
Press Enter.
Supercharge your spreadsheets with GPT-powered AI tools for building formulas, charts, pivots, SQL and more. Simple prompts for automatic generation.

Explanation:
- B2 is the starting cell for Electronics sales.
- COUNTA(B2:B13) dynamically counts all non-empty cells in the Electronics column, adjusting the height automatically.
- This formula sums all values in the “Electronics” column dynamically.
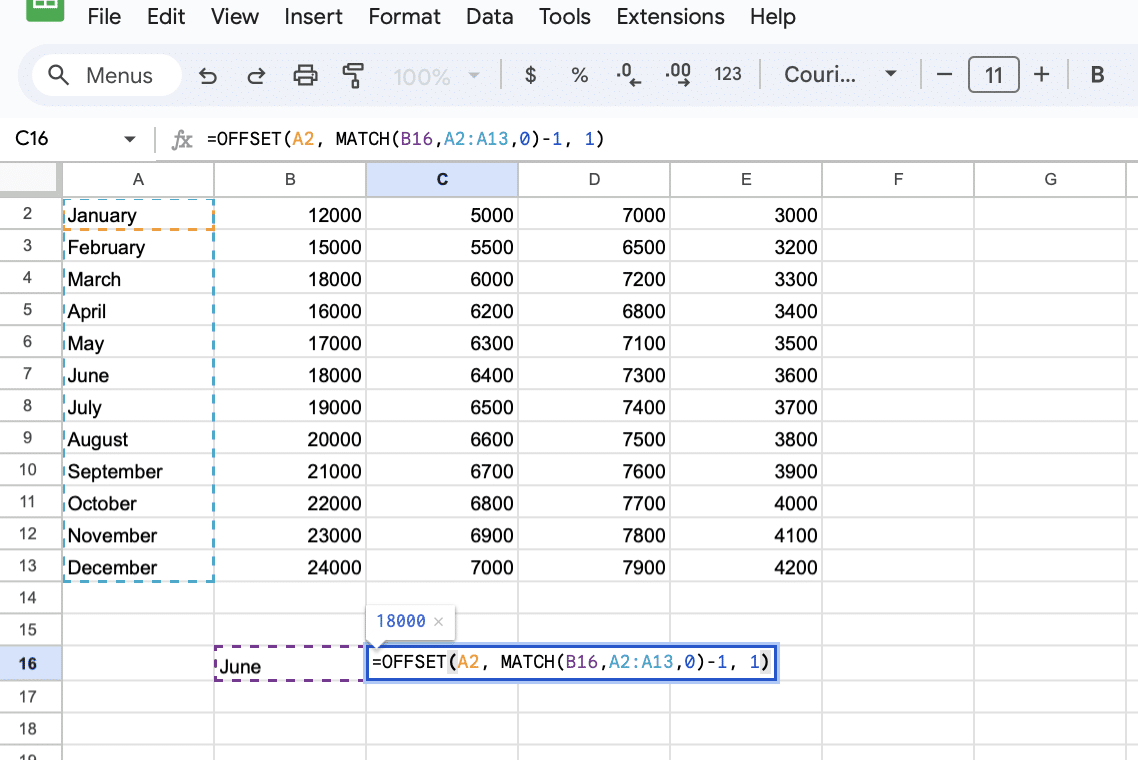
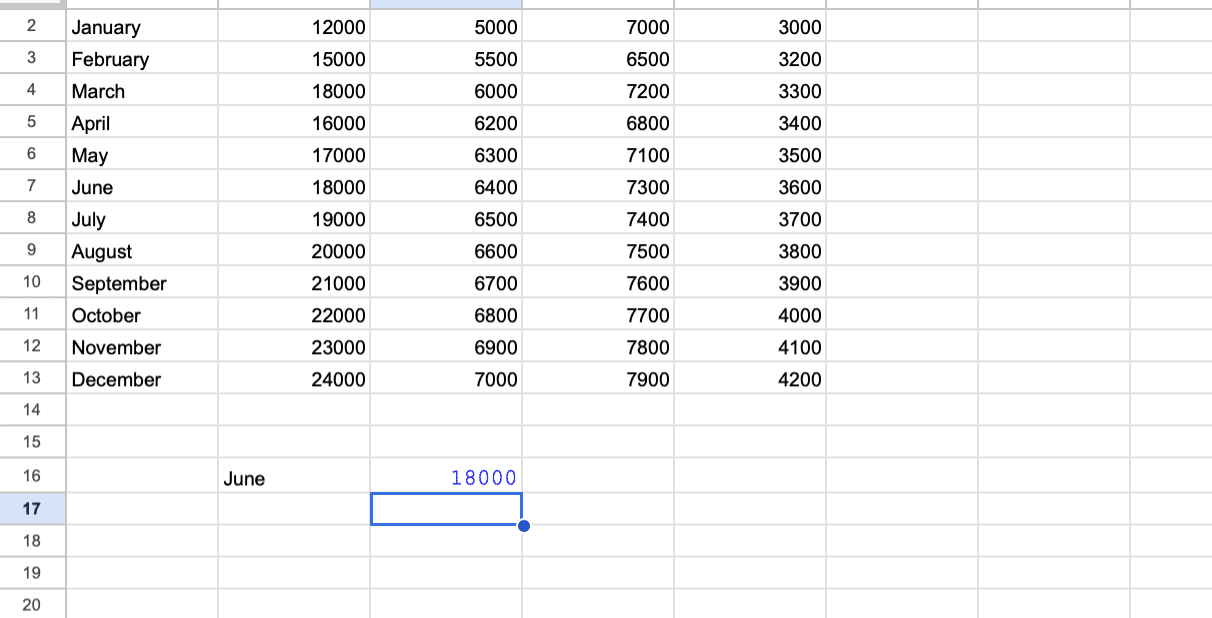
Conditional Data Extraction
Objective: Extract sales figures for a specific month using OFFSET and MATCH.
In a new cell, input the name of the month you want to search for (e.g., “July”).
In another cell, enter the formula: =OFFSET(A2, MATCH(A16,A2:A13,0)-1, 1)
Replace A16 with the cell where you’ve input “July.”
Explanation:
- MATCH(A16,A2:A13,0) finds the row number for “July.”
- OFFSET(A2,…,1) is offset to this row and one column right, returning the Electronics sales figure for July.
These steps demonstrate the versatility of the OFFSET function in Google Sheets, from handling dynamic ranges to integrating with other functions for complex data manipulations. Clear explanations, perhaps screenshots, should accompany each tutorial step to ensure readers can easily follow and understand how to leverage the OFFSET function in their spreadsheets.


