
Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor (or go to Tools > Macro > Visual Basic on Mac)
Insert a new module by going to Insert menu and selecting Module
Write your VBA code in the module editor
Run the code by clicking the Run button or pressing F5
The code will execute and perform the desired action in your Excel workbook
Want to learn how to use VBA in Excel? You’re in the right place!
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the basics of VBA in Excel, how to access the VBA editor, and the steps to start writing and running your own VBA code. By the end of this article, you’ll have the knowledge and confidence to take your Excel skills to the next level.
VBA in Excel 101: The Basics
VBA is a powerful programming language that is integrated into the Microsoft Office suite, including Excel. It allows you to automate repetitive tasks, create custom functions, and build complex applications within the Excel environment.
Some common uses of VBA in Excel include:
- Automating data entry and formatting tasks
- Generating reports and dashboards with dynamic data
- Developing custom tools and applications for specific business needs
- Integrating Excel with other Office applications, such as Word or PowerPoint
The VBA editor is the interface where you’ll write and manage your VBA code. It’s a separate window within Excel that provides a code editor, debugging tools, and other features to help you create and run your VBA scripts.
How to Open the VBA Editor in Excel
Accessing the VBA editor in Excel is a straightforward process, but the steps may vary slightly depending on whether you’re using a Windows or Mac computer.
On Windows:
- Open your Excel workbook.
- Press the Alt + F11 keys on your keyboard to open the VBA editor.
- The VBA editor window will appear, and you can start writing and running your VBA code.
On Mac:
- Open your Excel workbook.
- Go to the Tools menu and select Macro > Visual Basic.
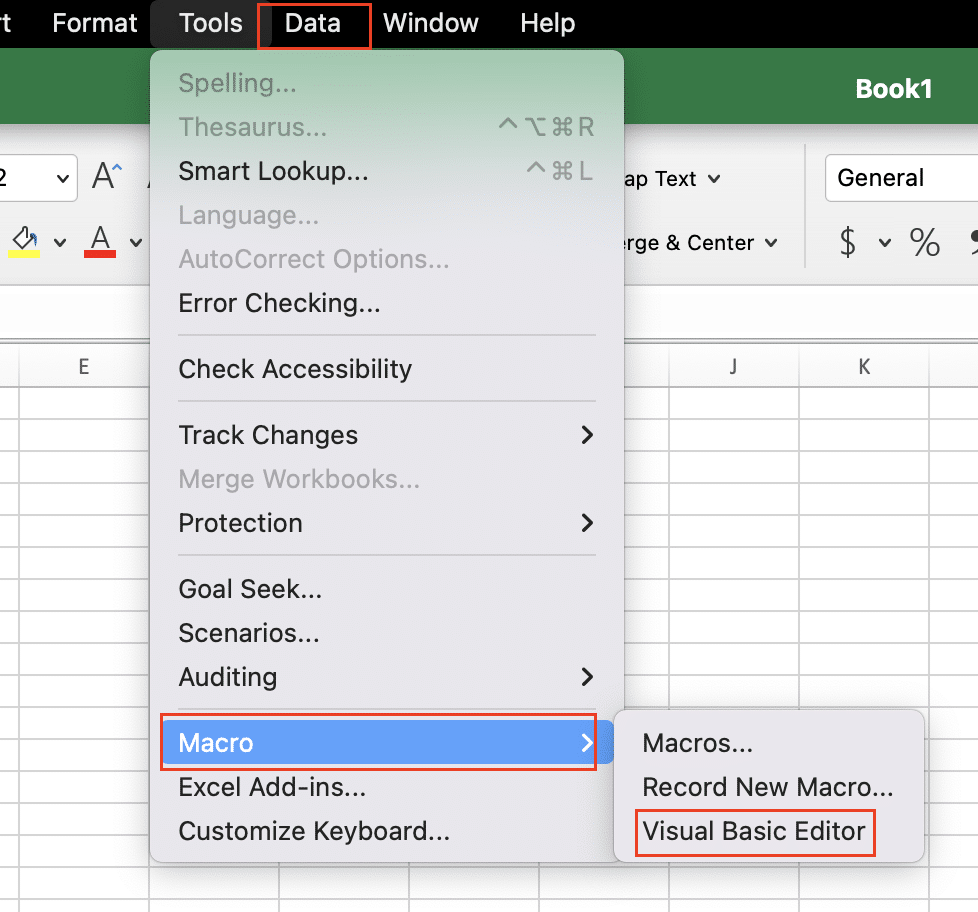
- The VBA editor window will appear, and you can start writing and running your VBA code.
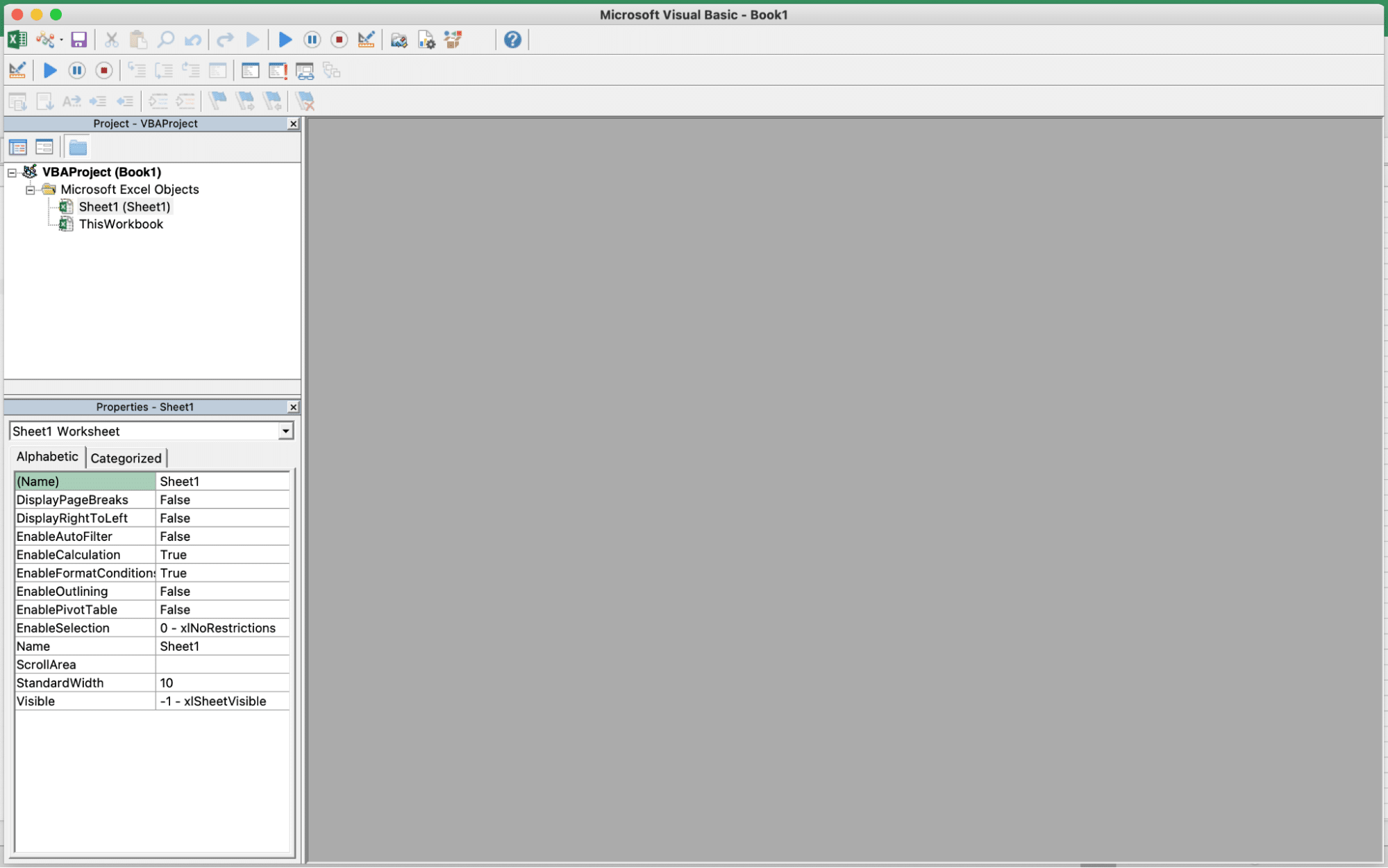
Once you’ve opened the VBA editor, you’ll see a project explorer on the left-hand side, which displays the various components of your Excel workbook, such as worksheets, modules, and user forms. This is where you’ll manage and organize your VBA code.
Inserting and Writing VBA Code in Excel
Now that you’ve accessed the VBA editor, it’s time to start writing your own VBA code. The process of inserting and writing VBA code in Excel involves a few simple steps:
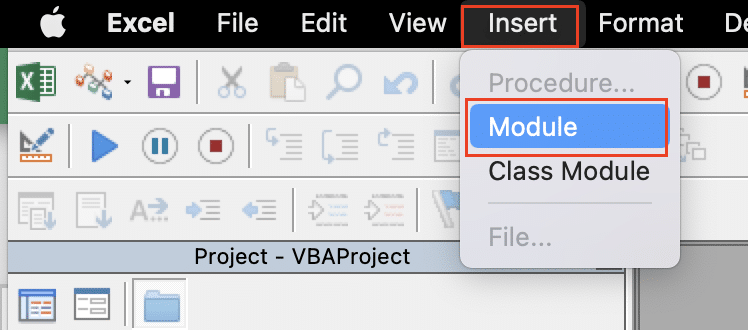
- Insert a new module: In the VBA editor, go to the Insert menu and select Module. This will create a new module where you can start writing your VBA code.
- Write your VBA code: In the code window, you can start typing your VBA code. VBA uses a syntax similar to other programming languages, such as Visual Basic or C#, so the code structure should be familiar if you have any prior programming experience.
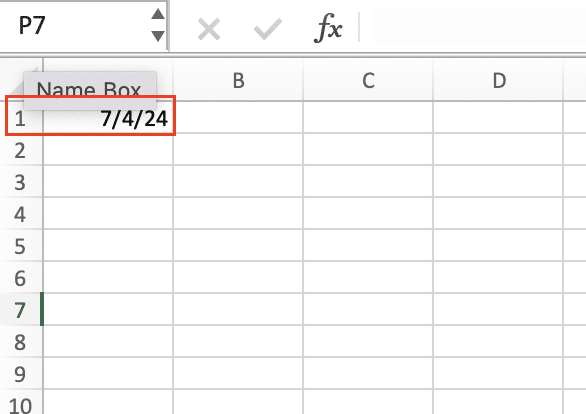
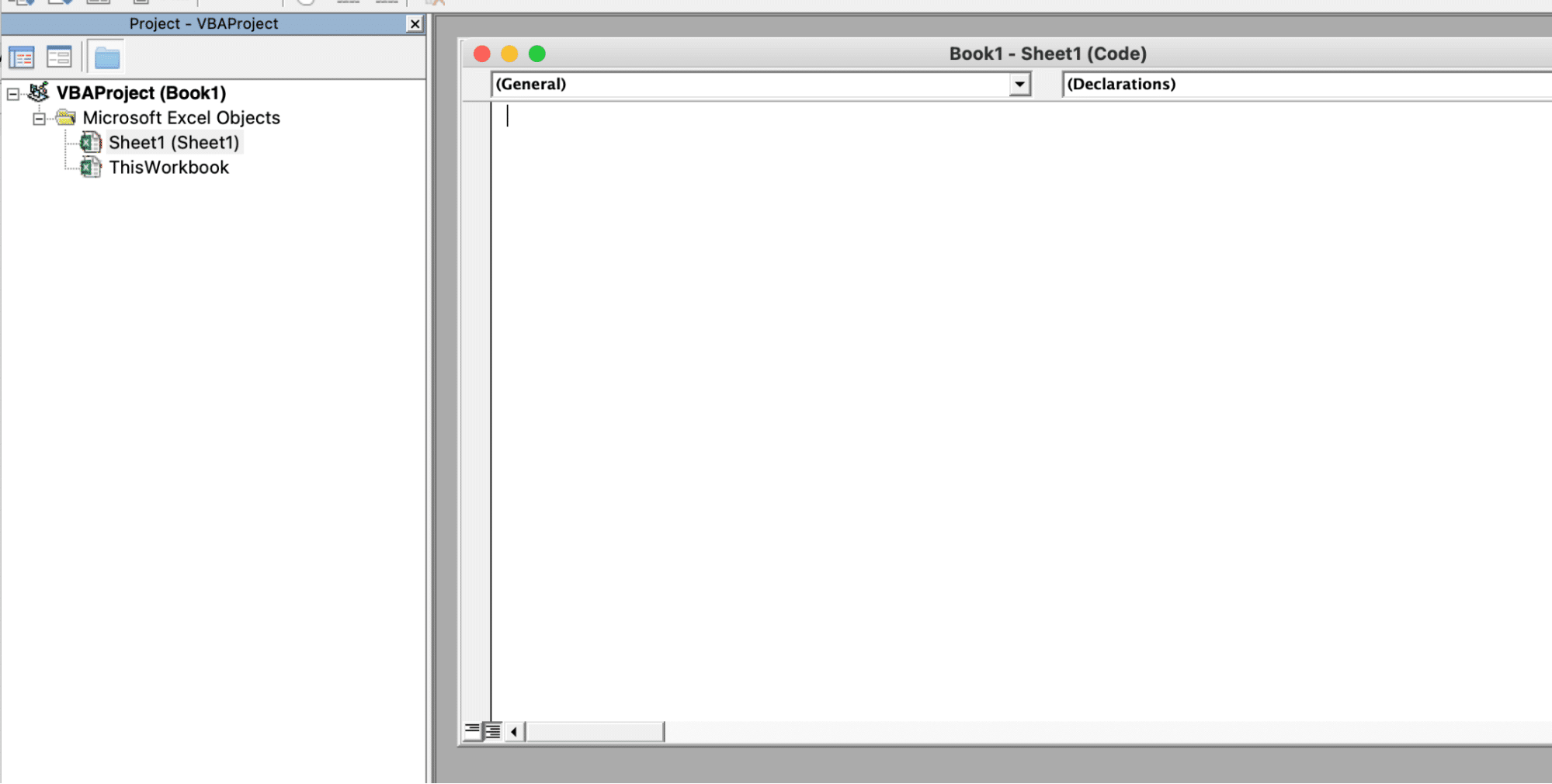
Here’s a simple example of a VBA script that will insert the current date in cell A1 of the active worksheet:
Sub InsertDate()
Range(“A1”).Value = Date
End Sub
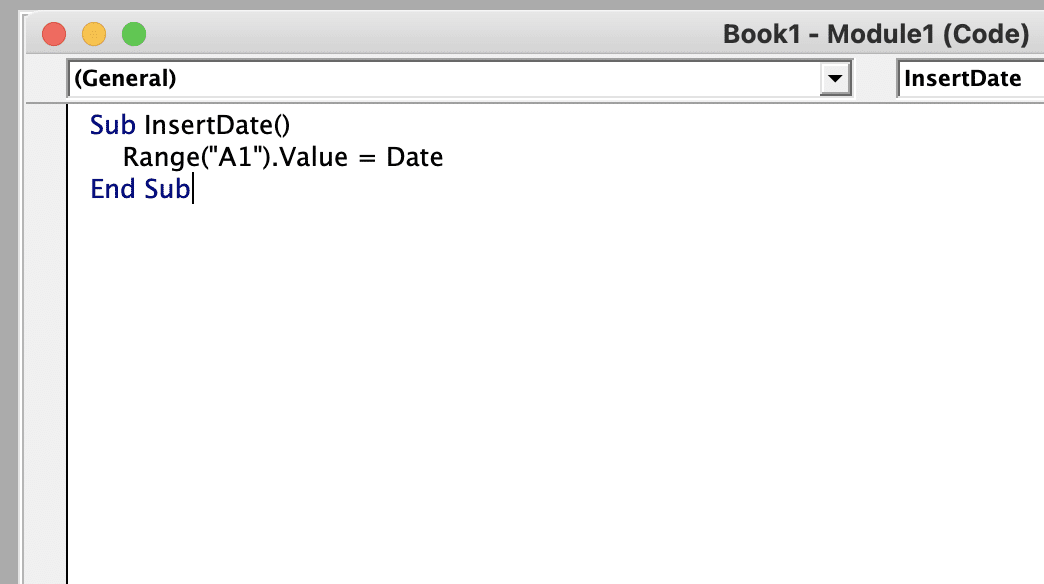
- Run your VBA code: Once you’ve written your VBA script, you can run it by clicking the Run button in the VBA editor toolbar or by pressing the F5 key on your keyboard. This will execute the code and perform the desired action in your Excel workbook.
As you become more comfortable with VBA, you can start exploring more advanced techniques, such as creating custom functions, building user forms, and integrating Excel with other Office applications. The possibilities are endless, and VBA can be a powerful tool to streamline your Excel workflows and boost your productivity.
Running VBA Code in Excel: Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you understand the basics of VBA, let’s dive into how to actually run your VBA code in Excel. There are a few different methods you can use to execute your scripts, depending on your needs and preferences.
Running VBA Code Manually
The most straightforward way to run your VBA code is to do so manually. Here’s how:

Stop exporting data manually. Sync data from your business systems into Google Sheets or Excel with Coefficient and set it on a refresh schedule.
Get Started
- Open the VBA Editor: To access the VBA Editor, press Alt + F11 or go to the Developer tab in your Excel ribbon and click on “Visual Basic.”

- Navigate to Your Code: In the VBA Editor, locate the module or sheet that contains your VBA code.

- Run the Code: With your code selected, click the “Run” button (the green play icon) or press F5 on your keyboard.
This method is great for quickly testing and debugging your code, as you can easily make changes and re-run it without having to save or close anything.
Executing VBA Scripts Using Buttons and Shortcuts
For a more user-friendly approach, you can create buttons or keyboard shortcuts to run your VBA code. This is especially useful if you have a script that you need to run frequently.
To create a button:
- Go to the Developer tab and click on “Insert” > “Button.”
- Draw the button on your worksheet where you want it to appear.
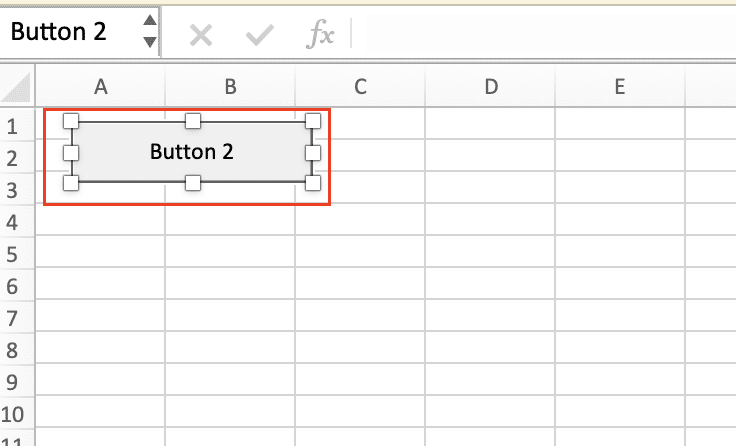
- Right-click the button and select “Assign Macro.” Choose the VBA subroutine you want to run.
For keyboard shortcuts:
- In the VBA Editor, right-click on the subroutine you want to assign a shortcut to and select “Customize.”
- In the Customize Keyboard window, choose the shortcut key you want to use and click “Assign.”
These methods make it easy for you or other users to quickly execute your VBA code without having to navigate to the VBA Editor every time.
Automating Tasks with VBA Macros
One of the most powerful features of VBA is its ability to automate repetitive tasks. By creating VBA macros, you can streamline your workflow and save time on tedious, manual processes.
To create a VBA macro:
- Open the VBA Editor and create a new module or select an existing one.
- Write the VBA code that performs the task you want to automate.
- Save the module and give the macro a descriptive name.
Once your macro is created, you can run it just like any other VBA code. You can also assign the macro to a button or keyboard shortcut for easy access.
Here are some examples of tasks that can be automated with VBA macros:
- Generating custom reports or dashboards
- Performing data analysis and manipulation
- Automating data entry and formatting
- Sending automated email notifications
- Integrating Excel with other applications
By leveraging the power of VBA macros, you can significantly improve your productivity and efficiency in Excel.
Beyond VBA: Automating Excel Without Code
Excel’s VBA allows for powerful automation, but it requires coding skills and can be challenging to maintain. Coefficient offers a no-code alternative for automating Excel tasks. It connects your spreadsheets to various data sources, allowing you to set up automated data imports, calculations, and report generation without writing VBA scripts. To see how you can automate Excel processes without coding, check out Coefficient.

