The #NAME? error in Excel occurs when the program can’t recognize a formula element you’re trying to use. This common error often appears when there’s a misspelling in a function name, a missing reference, or incorrect text formatting. Let’s explore every possible cause and solution to get your formulas working correctly.
Fix the #NAME? Error in Excel
Let’s walk through the complete process of identifying and resolving this error.
Step 1: Open and Locate the Error
- Open your Excel workbook
- Look for cells displaying the #NAME? Error
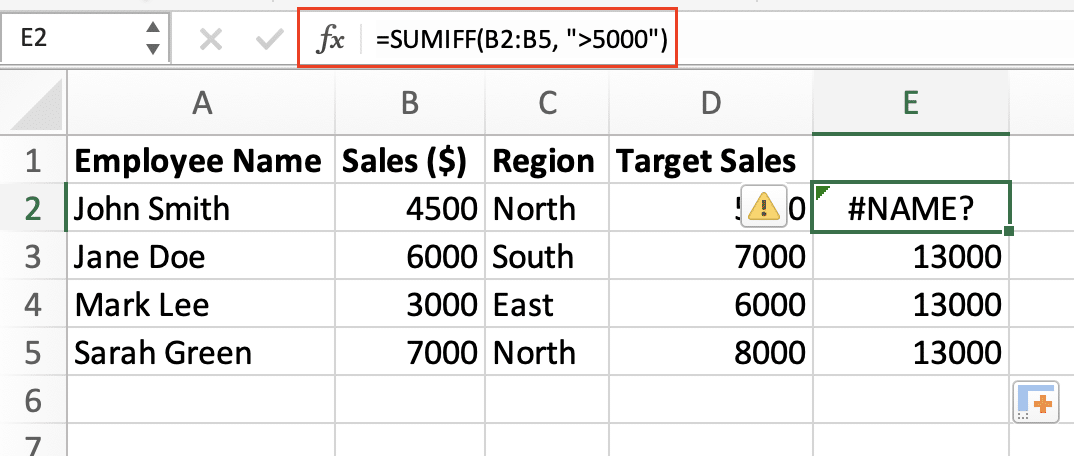
- Click on the affected cell to view the formula in the formula bar
- Note any patterns if multiple cells show the error
Tip: Use Excel’s Find feature (Ctrl + F) and search for “#NAME?” to locate all instances quickly.
Check and Correct Function Names
Function name misspellings are the most common cause of #NAME? errors. Here’s how to verify and fix them:
- Select the cell with the error
- Review the formula in the formula bar
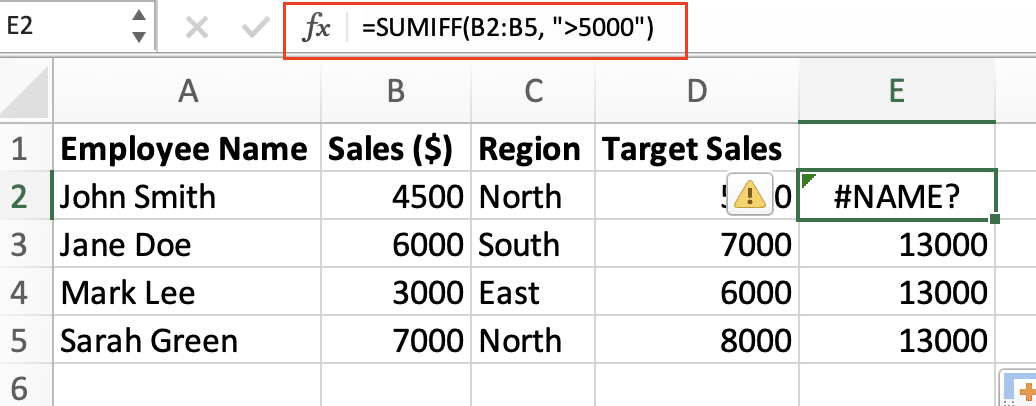
- Compare your function spelling with Excel’s official list
Here’s a reference table of commonly misspelled functions:
|
Incorrect Spelling |
Correct Spelling |
Function Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
SUMIF |
SUMIF |
Conditional sum |
|
Vlookup |
VLOOKUP |
Vertical lookup |
|
Sum |
SUM |
Addition |
|
AVrage |
AVERAGE |
Calculate average |
Pro Tip: Enable Formula AutoComplete (File > Options > Advanced) to prevent spelling errors.
Verify Named Range References
When using named ranges, follow these steps to ensure they exist:
- Go to the Formulas tab
- Click Name Manager
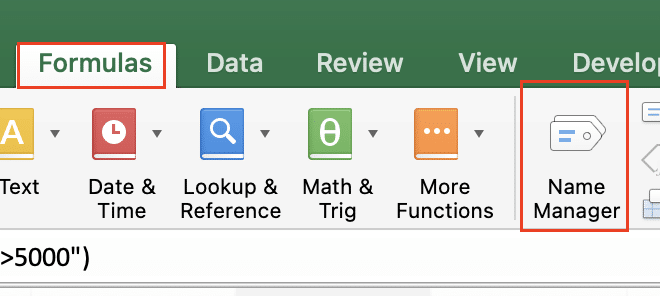
- Check if your referenced names appear in the list
- If missing:
- Create new named ranges
- Update existing references
- Delete obsolete names
Fix Text String Formatting
Text strings must be properly formatted to avoid #NAME? errors:
- Look for text without quotation marks
- Ensure you’re using straight quotes (“) not curved quotes (“)
- Add missing quotation marks
Example of correct text formatting:
|
Incorrect Formula |
Correct Formula 
Try the Free Spreadsheet Extension Over 500,000 Pros Are Raving About
Stop exporting data manually. Sync data from your business systems into Google Sheets or Excel with Coefficient and set it on a refresh schedule. Get Started |
Explanation |
|---|---|---|
|
=IF(A1=hello,1,0) |
=IF(A1=”hello”,1,0) |
Added quotes around text |
|
=CONCATENATE(First,Last) |
=CONCATENATE(“First”,”Last”) |
Added quotes around both strings |
Enable Required Add-ins
Some functions require specific add-ins. Here’s how to activate them:
- Navigate to File > Options > Add-ins
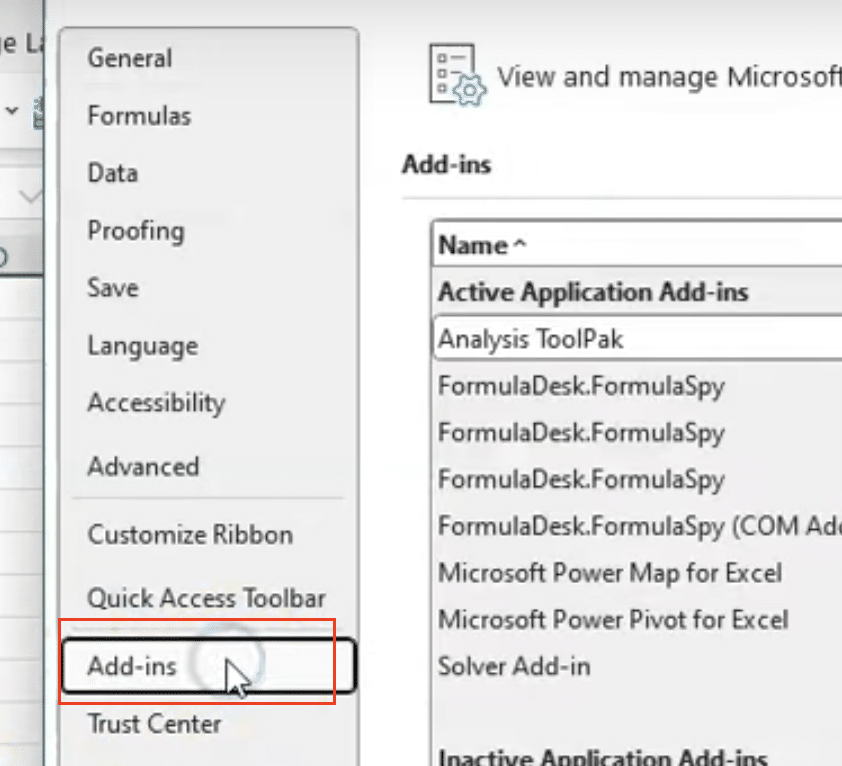
- Click ‘Go’ beside Manage Excel Add-ins
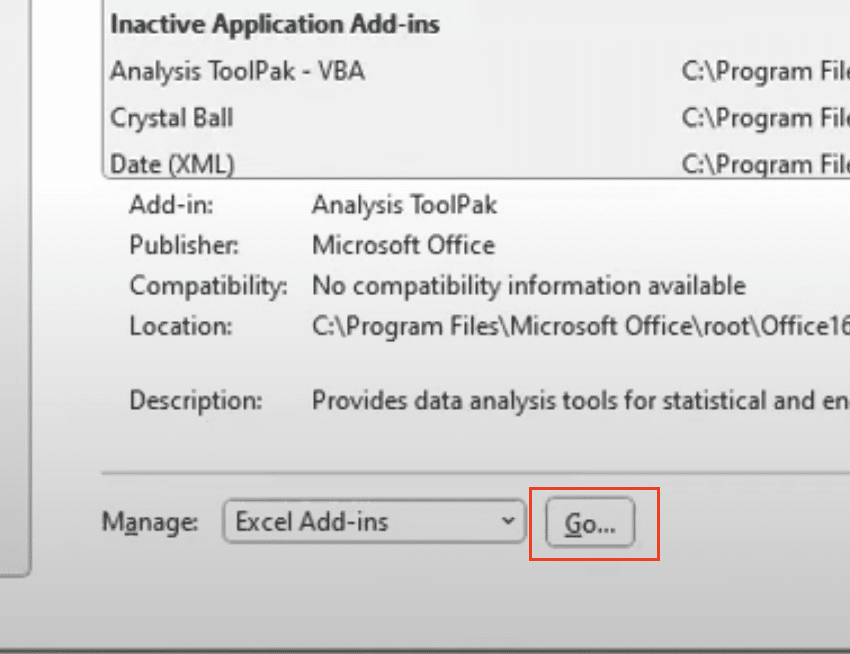
- Check boxes for needed add-ins:
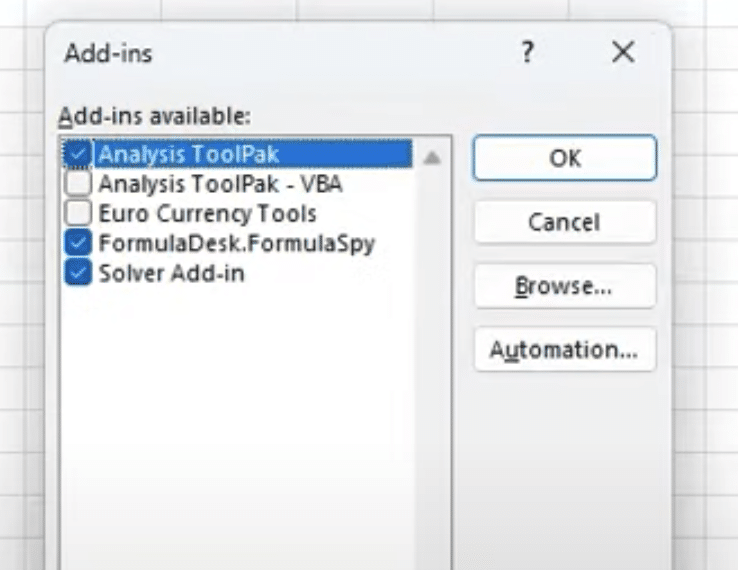
-
- Analysis ToolPak
- Solver
- Power Pivot
- Click OK to enable
Common Sources of #NAME? Errors
Prevent future errors by understanding these common causes:
- Undefined named ranges
- Missing quotation marks around text
- Incorrect function names
- Disabled add-ins
- Cross-workbook references to closed files
Formula Validation Techniques
Use these tools to troubleshoot complex formulas:
- Evaluate Formula tool:
- Select the cell
- Go to Formulas > Formula Auditing > Evaluate Formula
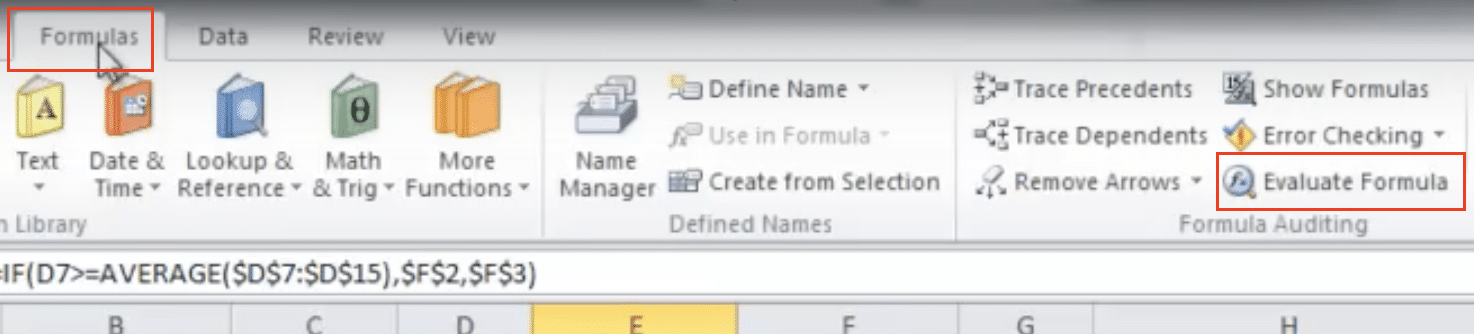
-
- Step through each part of the formula
- Break down complex formulas:
- Split into smaller parts
- Test each component separately
- Rebuild the formula step by step
Next Steps for Error-Free Formulas
Implement these best practices to maintain error-free worksheets:
- Regular formula auditing:
- Monthly formula checks
- Documentation of named ranges
- Consistent naming conventions
- Use Excel’s built-in tools:
- Formula AutoComplete
- Error checking options
- Name Manager
Your Excel Formulas, Error-Free
Now you have all the tools needed to fix and prevent #NAME? errors in Excel. Remember to check function names, verify named ranges, and properly format text strings. For more powerful Excel automation and error-free data management, try Coefficient’s integration tools.
Get started with Coefficient to streamline your Excel workflows and prevent formula errors before they happen.

