Excel macros let you record and replay sequences of commands, turning repetitive tasks into one-click operations. This guide shows you how to create, run, and customize macros to speed up your spreadsheet work.
Creating Your First Excel Macro
Before you start recording macros, you’ll need access to Excel’s Developer tab.
- Enable the Developer Tab:
- Open Excel Options (File > Options)
- Select ‘Customize Ribbon‘
- Check the ‘Developer‘ box in the right panel
- Click ‘OK’
- Record Your First Macro:
- Click ‘Developer’ > ‘Record Macro‘

- Enter a name (no spaces allowed)

- Assign a keyboard shortcut (optional)
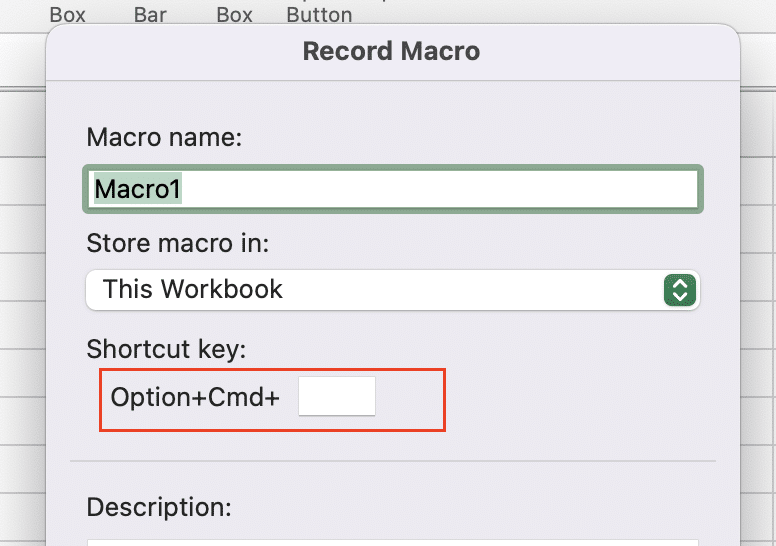
- Choose where to store the macro
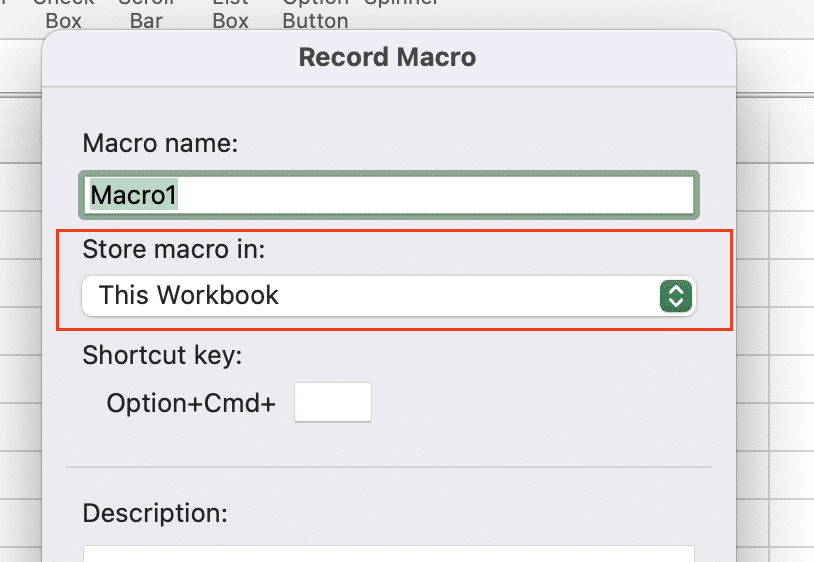
- Click ‘OK‘ to start recording
- Perform the actions you want to automate
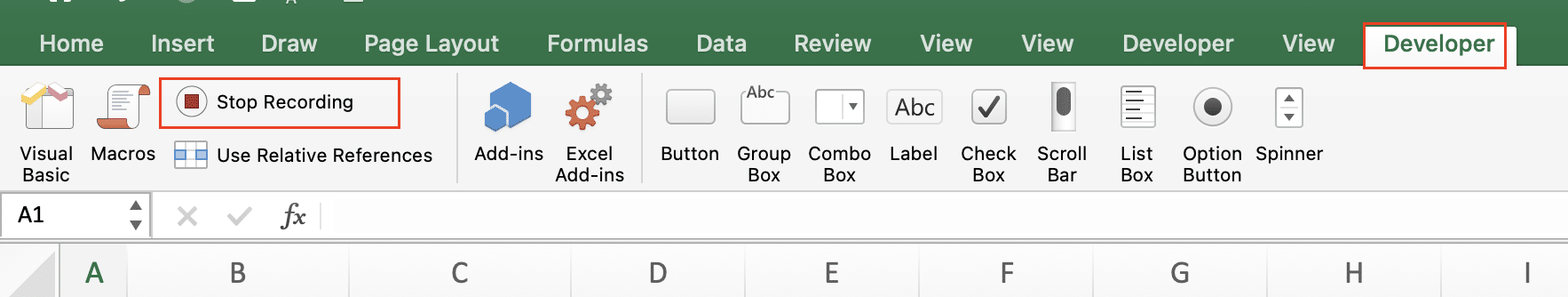
- Click ‘Stop Recording‘ when finished
Example macro settings:
|
Setting |
Example Value |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
Macro name |
FormatSalesReport |
Use clear, descriptive names |
|
Shortcut key |
Ctrl+Shift+F |
Choose unused combinations |
|
Store macro in |
This Workbook |
For single-file use |
How to Run and Modify Excel Macros
Running Macros Through Different Methods
You can run macros in three ways:

Stop exporting data manually. Sync data from your business systems into Google Sheets or Excel with Coefficient and set it on a refresh schedule.
Get Started
- Keyboard Shortcuts:
- Press your assigned shortcut combination
- Works instantly if macro is available
- Developer Tab:
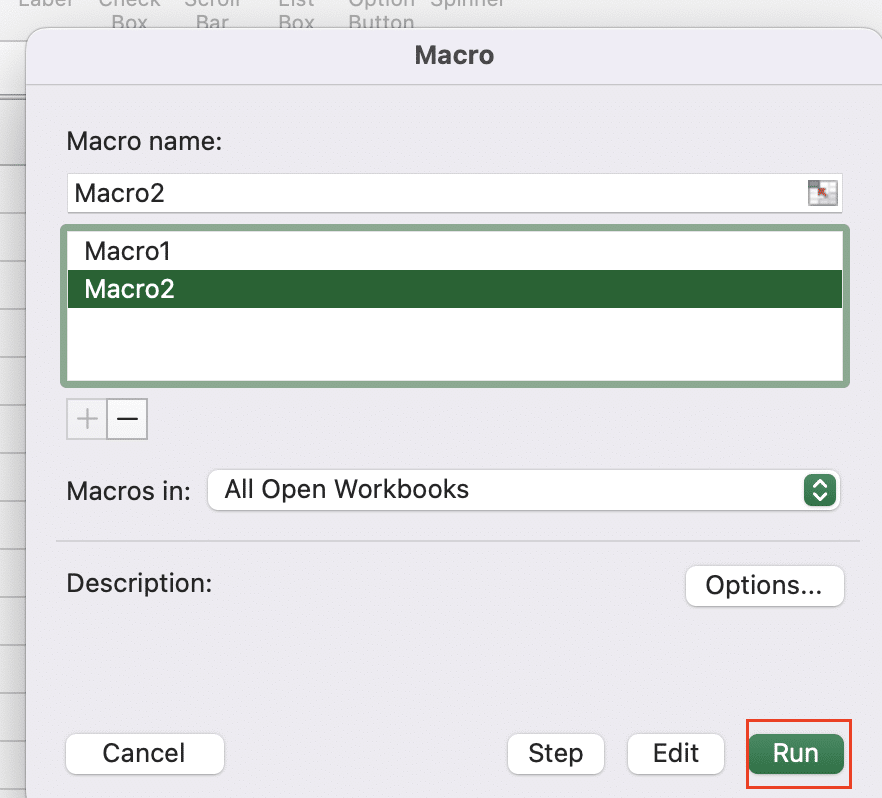
- Click ‘Developer’ > ‘Macros’

- Select macro name
- Click ‘Run’
- Quick Access Toolbar:
- Right-click macro button
- Select ‘Add to Quick Access Toolbar‘
- Click the toolbar button to run
Editing Existing Macros
To modify a macro:
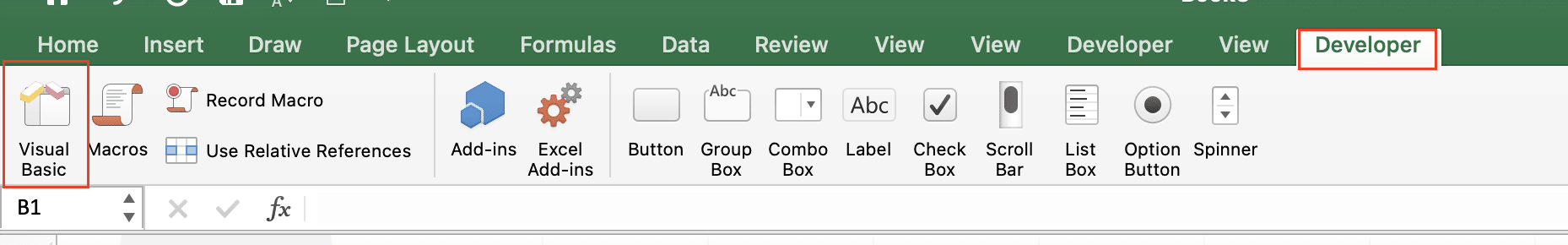
- Open Visual Basic Editor:
- Press Alt + F11
- Or click ‘Developer’ > ‘Visual Basic’
- Locate Your Macro:
- Expand ‘Modules’ in Project Explorer

- Double-click module containing macro
- Edit Code:
- Find Sub procedure with your macro name
- Modify VBA code as needed
- Save changes (Ctrl + S)
Essential Macro Security Settings
Macro security protects your system from potentially harmful code.
Required security steps:
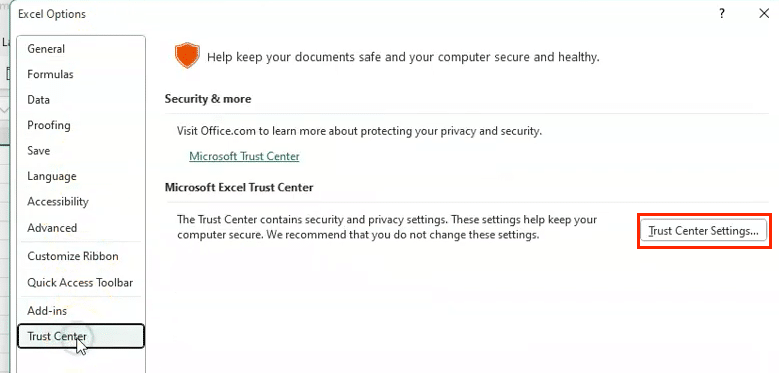
- Open Trust Center:
- File > Options > Trust Center

- Click ‘Trust Center Settings‘
- Choose Security Level:
- Disable all macros with notification (recommended)
- Enable macros from trusted locations
- Enable all macros (not recommended)
- Set Trusted Locations:
- Select ‘Trusted Locations‘
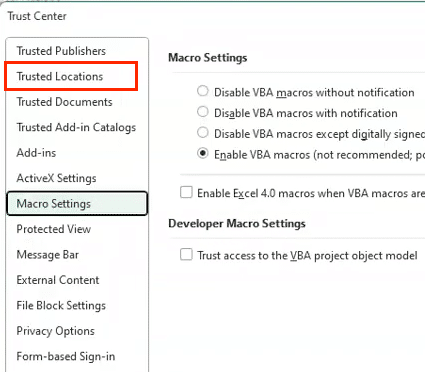
- Add folders for trusted macro files
Next Steps
Start with simple macros that handle basic tasks, then gradually build more complex automations. Practice recording and modifying macros to understand how they work. Remember to save your macro-enabled workbooks with the .xlsm extension.
Want to take your spreadsheet automation further? Try Coefficient to connect your Excel sheets directly to your business systems and automate data updates without macros.

