Accounting tasks are typically the last thing on business owners’ minds when they’re starting up or trying to grow their online business. For most entrepreneurs and leaders, accounting may not be their area of expertise, which can cause confusion when trying to ensure they’re maintaining accurate financial records and achieving tax compliance in their operating areas.
This can be particularly challenging for ecommerce sellers, as they’re shipping products across multiple jurisdictions and need to understand the nuances of each state’s regulations. While larger ecommerce companies typically have full departments dedicated to accounting practices, small businesses often need more support.
In this guide, we’ll walk through ecommerce accounting and bookkeeping for small businesses.
Detailed Guide: Ecommerce Accounting for Small Businesses
Before diving into our guide for ecommerce business owners, let’s define some essential terms that will help you understand accounting within your ecommerce business:
- Payroll – Payroll is the process of paying your employees based on their salary, hourly rate, and the labor laws of the area they reside or work. This may or may not be relevant to your small business depending on if you have employees or contractors that help operate your business.
- Accounts Payable – Payable is the process of receiving invoices from vendors, sending them through the appropriate approval flows and processing payment processing for those vendors.
- Billing/Accounts Receivable – Billing and accounts receivable is the process of generating invoices to send to customers for goods sold or services performed and then tracking payments received from customers and matching them against the invoices issued. Additionally, you may have a bookkeeper actively follow-up with customers to see when you should expect payment.
- Financial Reporting – Financial reports is the process of taking all of your ecommerce sales and summarizing them into relevant reporting for stakeholders. The most common financial statements are your income statement, balance sheet, or cash flow statements. Most organizations also have custom reporting to communicate in a more meaningful way to internal stakeholders.
- Sales Tax – Sales tax compliance is crucial for ecommerce sellers. They have to determine, on a regular basis, whether they have nexus in the jurisdictions they are shipping their product to. Nexus essentially means that they meet the criteria in that jurisdiction to file and pay sales tax.
Ecommerce and Accounting Platform
Two of the most important decisions in starting your ecommerce store and setting up the accounting processes are your choice of an ecommerce platform and an accounting system.
For their ecommerce platform, many small businesses use Shopify, which is common and user-friendly. If your business decides to use Shopify, linking to your accounting software will be straightforward. Shopify has pre-built connections with most major cloud-based accounting systems that a small business would use.
As for accounting software, small businesses use various platforms including:
- QuickBooks Online (QBO)
- Xero
- Sage
- Microsoft Dynamics
The good news is that almost all of these major cloud-based platforms will integrate with your ecommerce platforms like Amazon, eBay, and PayPal. In this example, we’ll walk through how Shopify can be connected with QuickBooks Online to help streamline your record-keeping.
To connect QuickBooks Online with your Shopify store, navigate to the apps section of the main menu.

Once you’ve selected the Apps section of the main menu, you can search for several applications integrated with Quickbooks Online, including Shopify.
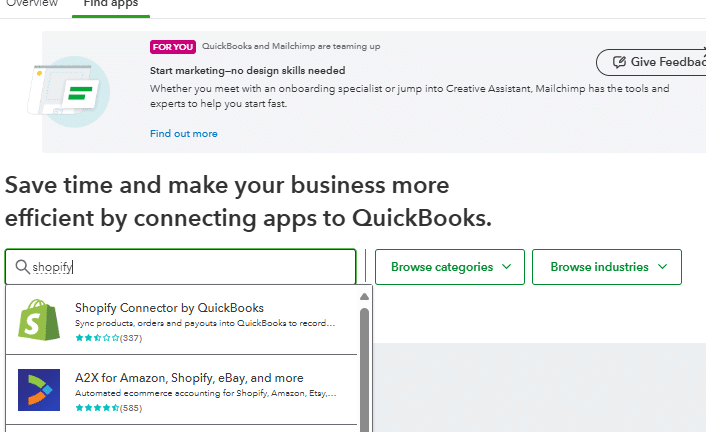
Now that you’ve selected the Shopify connector, you can link the Shopify app to your accounting software, Quickbooks Online. Note that there are several accounting software options that have as seamless of an integration to Shopify as Quickbooks Online.
Accounting Methodology
Once you have your systems in place and are ready to start processing financial transactions through your ecommerce platform and accounting system, you need to consider whether you will do accrual accounting or cash basis accounting.
- Cash Basis Accounting – This method is fairly straightforward and tied to when cash moves in and out of your business bank account. Under this method, you record financial transactions and recognize revenue and expenses when cash is received from your customers and paid out to your vendors. Typically, smaller businesses use this method because they won’t need an audit or financial review under United States Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Additionally, your income tax will more closely align with cash basis accounting.
- Accrual Method – Accrual accounting is more common in larger businesses or adopted by small businesses as they grow. In general, this method has you record transactions when they occur or have been earned, rather than when the cash has been paid out..
Accounts Payable
A vital process in ecommerce accounting is accounts payable. This is the process of generating a purchase, receiving an invoice, and paying vendors for goods or services. Typically, ecommerce business owners will generate a purchase order for inventory purchases and send it to their vendor.
While there are dedicated procure-to-pay and invoicing solutions in the marketplace, for small ecommerce companies your accounting software will be able to handle the invoice volume. In QuickBooks Online, for example, you can do this through the expenses section of the main menu.
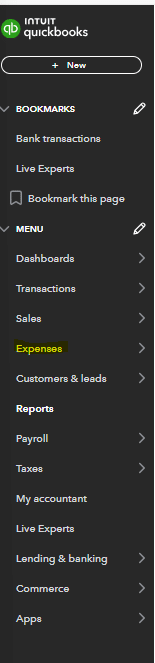
Within the expenses module you will have the ability to do several items. You can view expenses that have already been recorded and what account or category they were classified as. Additionally, there is the bills section within the expense module where you are able to add and pay bills. One major advantage of this is the ability to set-up recurring bills that generate automatically. To do this you:
Select the create recurring bill option in the add bill dropdown.

After selecting the recurring bill option, build out the bill with vendor and payment information. You’ll need to:
- Name the template
- Choose the vendor for payment
- Set up payment frequency
- Define start and end dates
This workflow automation is particularly helpful when setting up recurring bills for vendors with specific contract periods. The end date feature automatically stops payments when the contract ends, reducing human error in vendor management.
Next, categorize how you want the recurring bill coded in your general ledger by selecting the expense category and adding a description. This supports accurate bookkeeping and financial reporting.
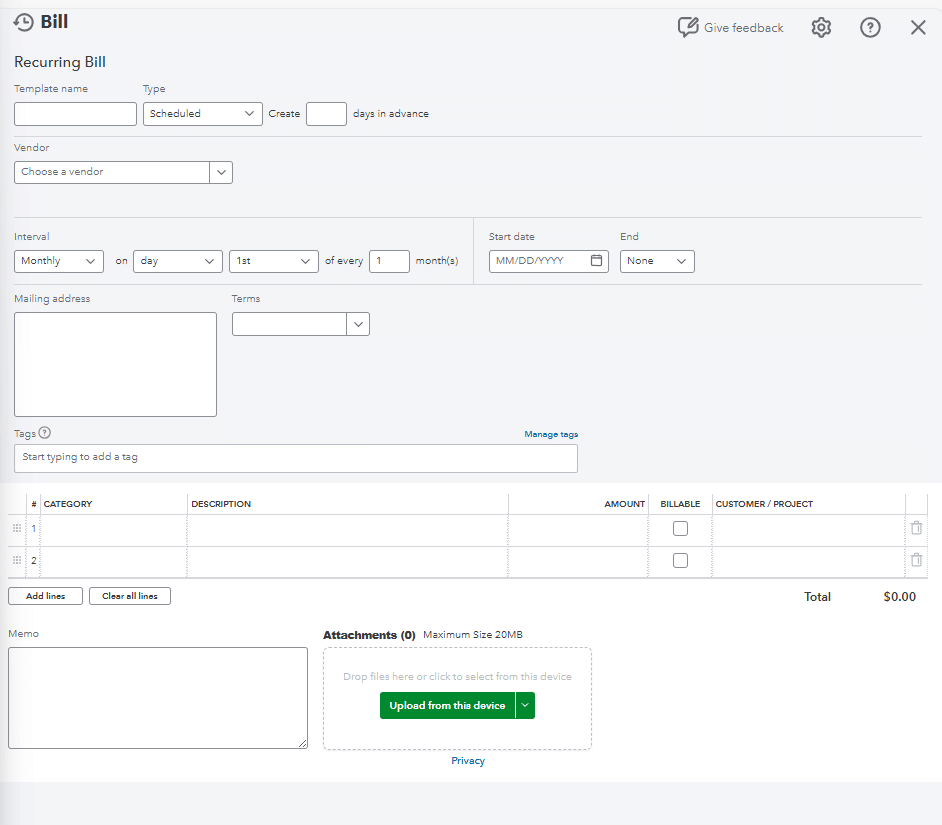
Beyond recurring bills, you can also:
- Create reminders for non-regular invoices
- Set up automated workflows for purchase orders
- Manage credit card payments
- Track vendor expenses in real-time
To set up automatic reminders in your QuickBooks Online account for upcoming bills, select “reminder” as the type instead of “scheduled.” This allows your team to review and adjust amounts or dates as needed.
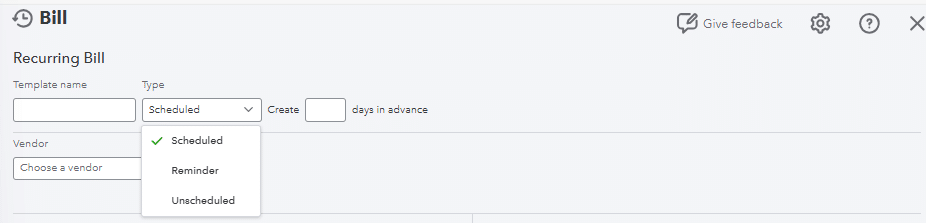
You can also automate the template creation and set it to unscheduled in the type dropdown. This is useful for infrequent vendor payments, saving less time on repetitive setup tasks.
By using the functionality within your accounting software to automate and make running your ecommerce business easier and more efficient, you will be better off. As your business grows you may want to consider a separate procure-to-pay solution such as SAP Ariba or Coupa, but for small businesses that is unnecessary and isn’t cost-effective.
Accounts Receivable
Similar to accounts payable, accounts receivable is crucial for ecommerce sellers. Fortunately, for ecommerce businesses using a direct-to-consumer model, there aren’t many sales awaiting payment since consumers pay at the time of purchase. However, it’s still important to have your billing and accounts receivable processes in place to appropriately charge and recognize revenue from online sales.
For small businesses, it’s most efficient to generate your sales orders and invoices in your ecommerce platform. If you’re using Shopify, you would generate your sales order there, feed it through to your inventory management system to ship, and also feed it into your accounting system.

Stop exporting data manually. Sync data from your business systems into Google Sheets or Excel with Coefficient and set it on a refresh schedule.
Get Started
Once the invoice has been fed into your accounting software, you can match the corresponding payment from your customer to that invoice and clear it from your accounts receivable. This approach helps your small business:
- Maintain accurate tracking of all financial transactions
- Ensure proper tracking inventory across your online store
- Streamline processing of payment gateways transactions
- Efficiently handle refunds and adjustments
- Maintain real-time synchronization with your accounting system
Financial Reporting and Statements
Once you have your systems set up, have selected your accounting method, and are managing payments correctly, you will have accurate financial information to report. Financial reporting is how you tell the financial story of your business to help communicate with stakeholders and support business decisions.
The essential financial reports that every ecommerce business should generate regularly are:
- Profit and Loss Statement – This measures the profitability of your business during a specific period, including your cost of goods sold and profit margins. The results will vary depending on whether you’re using cash basis or accrual method accounting.
- Balance Sheet – This report measures your assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. For ecommerce companies, one important measure from your balance sheet is working capital – your current assets minus current liabilities, measuring your business finances and short-term liquidity.
- Cash Flow Statements – This tracks your cash flow management from operating, investing, and financing activities during a specific period. It’s especially valuable for bridging the gap between accrual accounting and actual cash position.
- Aged Accounts Receivable – This details all customer outstanding invoices. This report may not be needed if you’re always paid at time of sale.
- Aged Accounts Payable – Similar to receivables, this shows all outstanding vendor invoices, helping you prioritize payments and manage your business finances.
Sales Tax Compliance
One of the most complex areas for an ecommerce business is managing sales tax compliance and ensuring you’re compliant across all jurisdictions where you operate or ship. Whether a business must file and pay sales tax in a certain state is based on their nexus.
Depending on the state, sales tax can be taxed in two ways:
- Origin-based sales – determined by seller location
- Destination-based sales – determined by buyer location
For example, thresholds for nexus vary by state:
Arkansas:
- $100,000 in ecommerce sales in current or previous calendar year
- 200 transactions in current or previous calendar year
California:
- $500,000 in sales in current or previous calendar year
- Mixed taxing jurisdictions with city, county, and state taxes
- Physical nexus if you maintain inventory or office locations
Delaware:
- No sales tax
Once you determine your tax obligations, you’ll need to register in each state. This is where specialized tax compliance software can help. Major providers like TaxJar and Avalara can:
- Show which states require registration based on your sales data
- File and pay your tax returns
- Automate compliance processes
Another sales tax area that ecommerce businesses will want to look into is whether or not they have any sales tax exemptions. The most common sales tax exemptions are:
- Production exemption – This applies when a specific product is not taxable. These exemptions will vary by state. The most common exemptions are for food, clothing, supplements, etc.
- Customer exemption – This applies when there is a specific type of customer that is exempt from paying sales tax. The most common example of this is non-profit organizations such as a school, church, government agency, etc. In order to ensure that your ecommerce business is not being charged sales tax, due to a customer exemption, is to present your sales tax exemption certificate to your vendors.
- Transaction exemption – This applies when you are selling your product to a distributor who will then resell that product to the end-user. These type of transactions are typically tax exempt so sales tax is only paid once for the product to the end-user. In this scenario you would need to obtain a resale sales tax exemption certificate.
For ecommerce businesses the most common sales tax exemption they are eligible for is a production exemption. If you are an ecommerce business shipping a product that may be exempt it can eliminate the need for you to charge, collect, and pay sales tax on behalf of your customers.
Benefits of Optimizing Accounting within your Small Ecommerce Business
- Seamless integration between your ecommerce and accounting software to minimize manual touches and errors.
- Compliance with all of the relevant sales tax laws in each state to ensure you don’t have unknown liabilities within your business.
- Financial reporting that can help drive business decisions and make the business more profitable and grow.
- Accurate billing and timely payment to vendors to ensure you are collecting payments in a timely manner and paying your vendors.
Improve Ecommerce Accounting in Your Small Business
As online sales continue to grow, proper accounting tasks and tax compliance become increasingly important. Following this guide and utilizing tools can help your business grow while maintaining proper financial records. One tool that can help tell your financial story is Coefficient, which seamlessly integrates with QuickBooks Online and helps non-financial people understand financial data.
Ready to transform your ecommerce accounting?
Try Coefficient to seamlessly integrate your Excel with live data from various business systems, enabling real-time analysis and more advanced financial modeling.

