Gong, the revenue intelligence platform, captures crucial insights from your sales calls. But what if you could bring that data directly into Microsoft Excel?
By importing live Gong data directly into your spreadsheets, you’ll gain real-time insights into your sales calls, scorecards, and team performance. This no-code Gong integration eliminates manual export data processes and streamlines your workflows. The API-powered connection through Coefficient makes it simple to automate data syncing without the complexity of Zapier or other connectors.
Let’s dive into how you can set up this powerful integration and transform your sales data analysis.
Prefer video? Watch the tutorial here!
Advantages of Using Excel with Gong Data
- Centralized Analysis & Automation: Automate the flow of Gong data into Microsoft Excel and combine it with other sales metrics from your CRM in one place. Build workflows that eliminate repetitive tasks. Custom Reporting: Create tailored dashboards and reports using familiar Microsoft Excel tools without writing SQL queries or managing a data warehouse. Advanced Data Manipulation: Apply Microsoft Excel‘s robust functions and formulas to your Gong dataset. Access powerful analysis capabilities beyond what Zapierworkflows offer. Historical Tracking: Maintain and analyze trends in your Gong data over time with automatic notifications when new data arrives. No-Code Integration: Unlike Zapier or low-code platforms, Coefficient provides a native Microsoft Excel experience. Connect multiple data sources including SharePoint and other business systems without technical expertise—no API knowledge required.
Step-by-Step Tutorial: Connecting Gong to Excel
Step 1: Install Coefficient in Excel
Before diving in, ensure you have the Coefficient add-in installed in Microsoft Excel.

Stop exporting data manually. Sync data from your business systems into Google Sheets or Excel with Coefficient and set it on a refresh schedule.

- Open Excel from your desktop or in Office Online. Click ‘File’ > ‘Get Add-ins’ > ‘More Add-Ins.’
- Type “Coefficient” in the search bar and click ‘Add.’
- Follow the prompts in the pop-up to complete the installation.
- Once finished, you will see a “Coefficient” tab in the top navigation bar. Click ‘Open Sidebar’ to launch Coefficient.
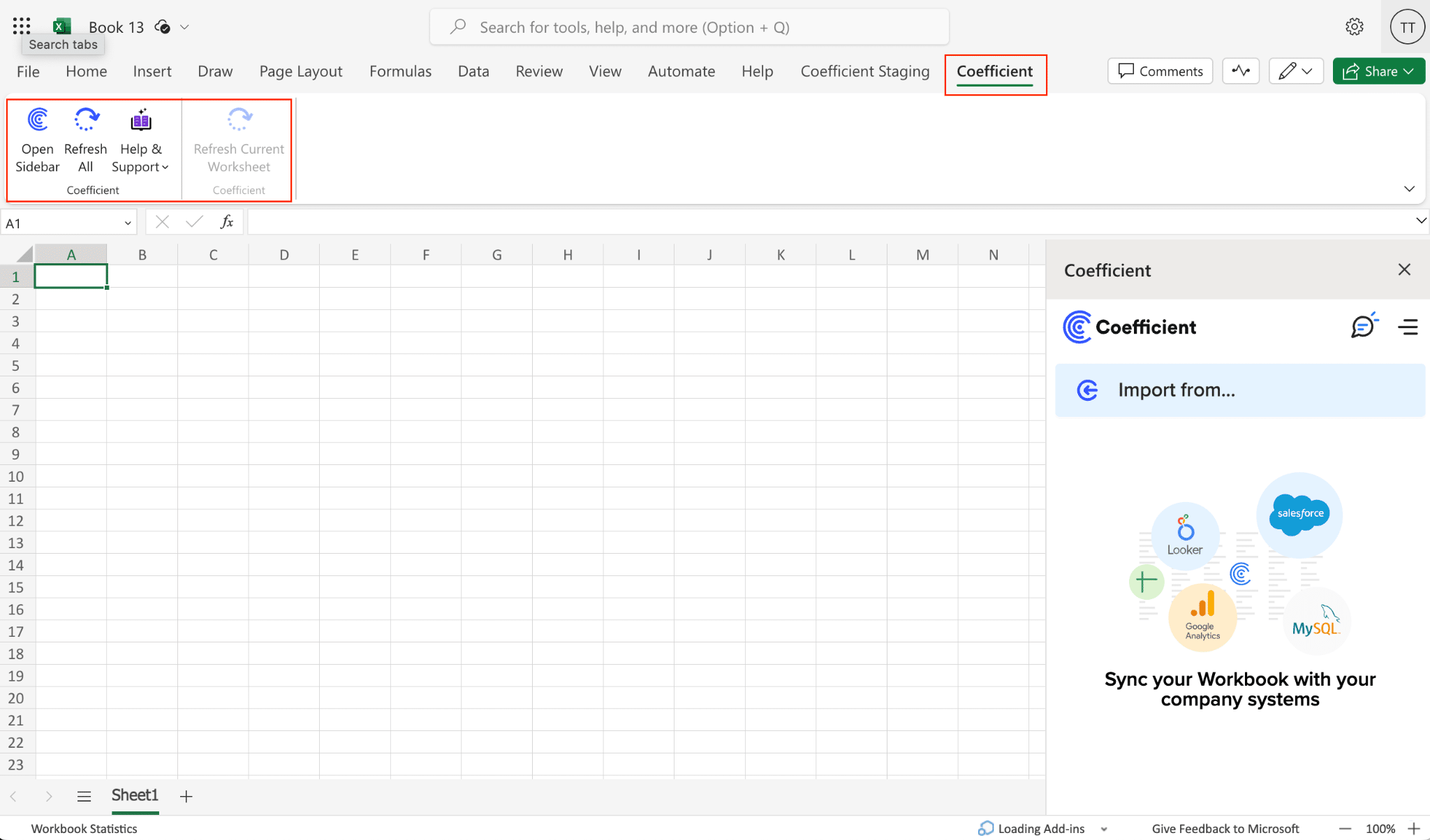
Step 2: Add Gong as a Data Source
- Open Microsoft Excel and launch the Coefficient add-in from the ribbon. In the Coefficient sidebar, click “Add a Data Source“.
- Search for “Gong” in the list of Gong integrations and select it.
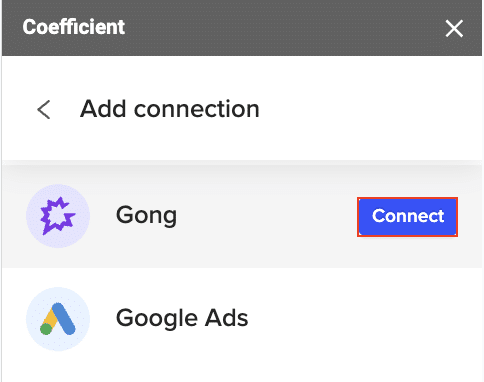
Step 3: Connect Coefficient to Your Gong Account
- Open a new tab and log into your Gong account.
- Copy your Gong account name from the URL, and paste it into Coefficient.

- Click “Authorize” and grant the necessary permissions when prompted. Coefficient uses secure API authentication to establish the connection to your workspace.

Step 4: Initiate Your First Import
- After authorization, return to Gong and click “Start from Scratch”.
- In the import preview, select the type of Gong dataset you want to import (e.g., calls, scorecards, logs, workflow data).
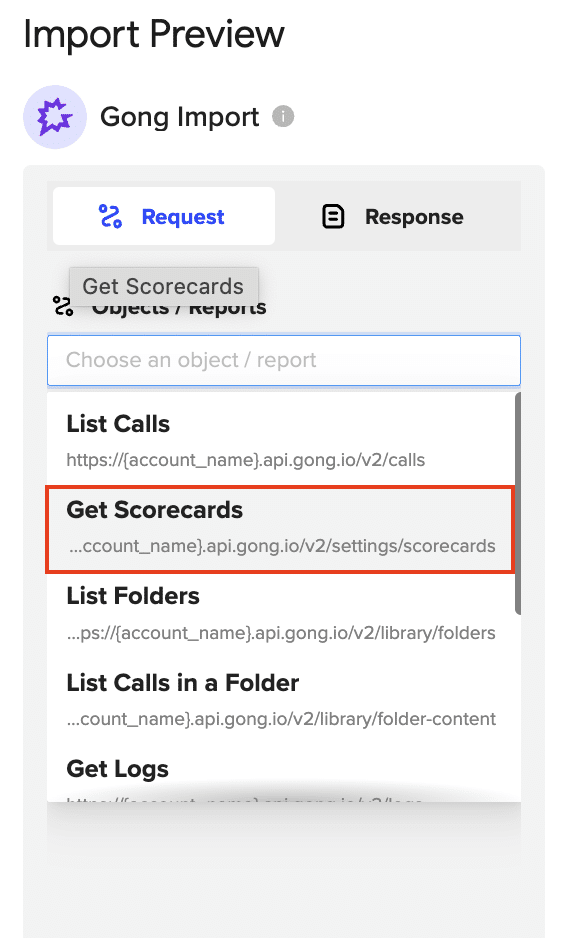
Step 5: Customize Your Data Import
- For this example, let’s import scorecards. Select “Get Scorecards” and click “Preview”.
- Choose the fields you want to import into Microsoft Excel.
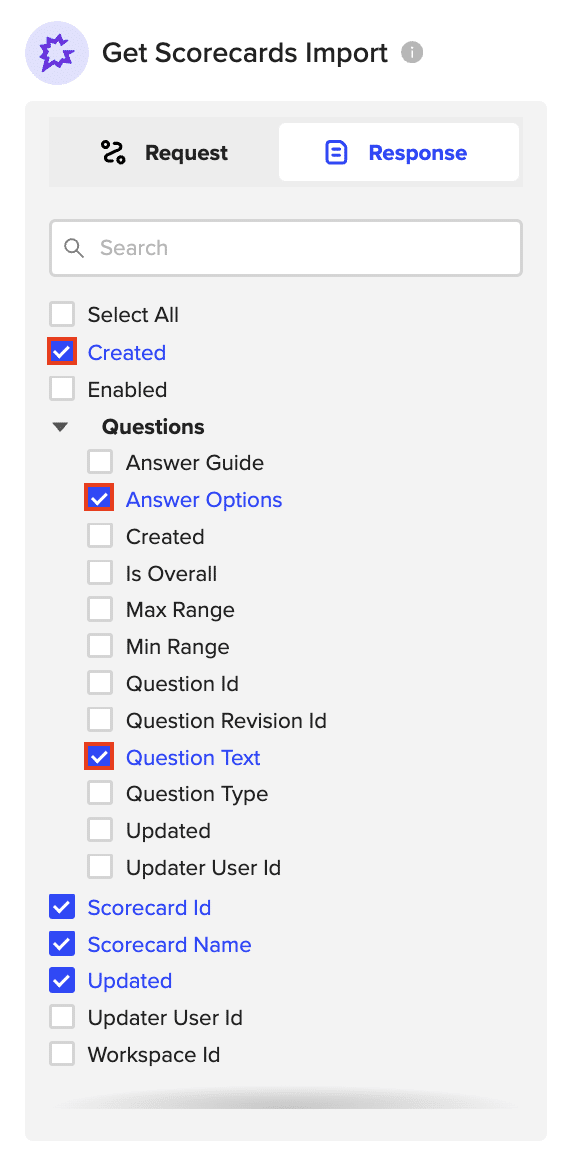
Step 6: Import and Set Up Auto-Refresh
- Once you’re happy with your selection, click “Import”.
- Configure an auto-refresh schedule to keep your Gong data up-to-date automatically. Set up notifications to alert you when new data syncs, ensuring your Microsoft Excel dashboards always reflect the latest information.

Use Cases for Managing Gong Data in Excel
- Call Volume Analysis: Import call data for specific date ranges to track sales team performance over time. Create pivot tables and charts in Microsoft Excel to visualize trends and patterns in call activity.
- Scorecard Performance Tracking: Use imported scorecard data to identify top-performing team members and areas for improvement. Build custom Microsoft Excel formulas to calculate success rates and highlight exceptional results. Automate weekly workflows to share insights with leadership.
- Workspace Auditing: Retrieve workspace details to manage and organize your Gong environment effectively. Use Microsoft Excel‘s filtering and sorting capabilities to quickly find relevant information.
- Competitor Mention Tracking: Import tracker details to monitor when competitors are mentioned during calls. Create conditional formatting rules in Microsoft Excel to highlight these instances for easy review.
- Team-Specific Call Analysis: Utilize the “Get calls in folder” endpoint to analyze call activity for specific sales teams or deals. Build dynamic Microsoft Exceldashboards that update automatically as new data is imported.
For more advanced use cases, you can sync Gong data to a data warehouse using reverse ETL patterns, integrate with your CRM or SharePoint systems, or run SQL queries across combined datasets. This no-code approach offers flexibility that rivals Zapier workflows but with the familiar power of Microsoft Excel. Consider the pricing efficiency: instead of maintaining multiple Zapier connections or low-code platforms, Coefficient provides an all-in-one solution for your data sources.
Connect Gong to Excel in Seconds with Coefficient
Connecting Gong to Microsoft Excel through Coefficient opens up a world of possibilities for analyzing and reporting on your sales call data. Unlike Zapier workflows that require multiple steps and connectors, this Gong integration provides a direct, no-code path to automate your data analysis. By following this guide, you’ve learned how to import Gong data into Microsoft Excel, keeping it fresh with auto-refreshes.
Now you can combine Gong’s powerful call insights with Microsoft Excel‘s analytical capabilities to drive your sales performance to new heights. Whether you’re building dashboards, syncing to a data warehouse, or creating custom workflows, Coefficient gives you the tools to work smarter. Ready to supercharge your Gong data analysis? Get started with Coefficient today and transform how you work with your sales call data in Microsoft Excel.


