Managing dates and times in Excel can be challenging, especially when dealing with complex calculations or automated reporting. This comprehensive guide will walk you through Excel’s essential date and time functions, showing you how to implement them effectively for business applications. Whether you’re tracking project deadlines, calculating employee hours, or automating report timestamps, these functions will help streamline your workflow.
Creating and Manipulating Dates in Excel
How to Insert Current Date and Time
Let’s start with the basic functions for inserting dates and times into your spreadsheets.
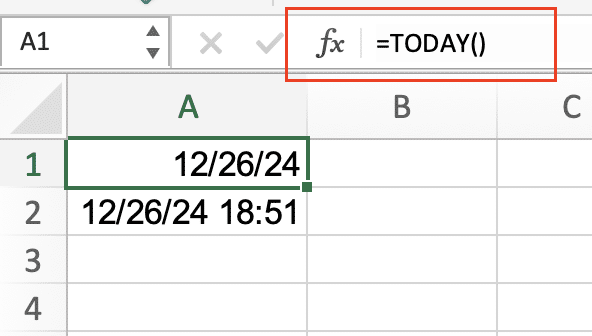
Using TODAY() and NOW()
The TODAY() and NOW() functions are fundamental for working with current dates and times:
|
Function |
Example |
Result |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
TODAY() |
=TODAY() |
1/15/2024 |
Returns current date |
|
NOW() |
=NOW() |
1/15/2024 13:45:30 |
Returns current date and time |
Quick Keyboard Shortcuts
- Current Date: Press Ctrl + ;
- Current Time: Press Ctrl + Shift + ;
Converting Text to Dates Use the DATE function to construct dates from separate year, month, and day values:
|
Formula |
Result |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
=DATE(2024,1,15) |
1/15/2024 |
Creates date from components |
|
=DATE(YEAR(TODAY()),1,1) |
1/1/2024 |
First day of current year |

Working with Date Components
Extracting Date Parts
|
Function |
Example |
Result |
|---|---|---|
|
=YEAR(“1/15/2024”) |
2024 |
Extracts year |
|
=MONTH(“1/15/2024”) |
1 |
Extracts month |
|
=DAY(“1/15/2024”) |
15 |
Extracts day |

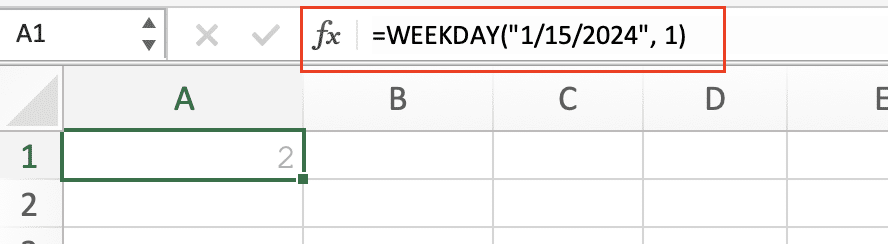
Weekday Calculations The WEEKDAY function returns a number representing the day of the week:
excel
=WEEKDAY(“1/15/2024”, 1) // Returns 2 (Monday = 1, Sunday = 7)

Stop exporting data manually. Sync data from your business systems into Google Sheets or Excel with Coefficient and set it on a refresh schedule.
Get Started
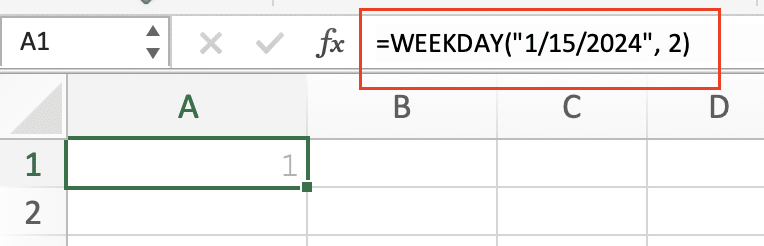
=WEEKDAY(“1/15/2024”, 2) // Returns 1 (Monday = 1, Sunday = 7)
Date Arithmetic Add or subtract days using simple arithmetic:
|
Operation |
Formula |
Result |
|---|---|---|
|
Add Days |
=TODAY()+5 |
Date 5 days from today |
|
Subtract Days |
=TODAY()-5 |
Date 5 days ago |
Time Calculations and Formatting
Basic Time Operations
Converting Time to Decimal Hours
|
Formula |
Result |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
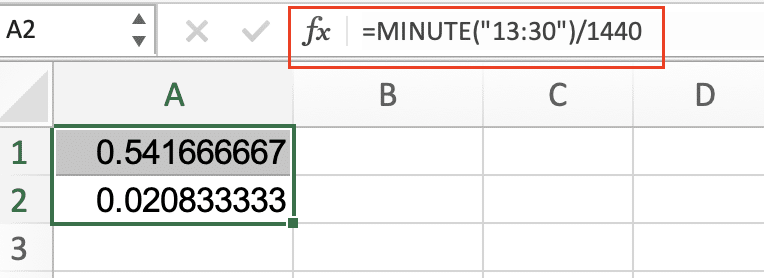
=HOUR(“13:30”)/24 |
0.5625 |
Converts time to decimal |
|
=MINUTE(“13:30”)/1440 |
0.0208 |
Minutes as decimal |
Time Differences
excel
=TIME(13,30,0) – TIME(9,15,0) // Returns 4:15:00 (4.25 hours)

Next Steps
Now that you understand Excel’s date and time functions, start implementing them in your workflows. Begin with basic functions like TODAY() and NOW(), then progress to more complex calculations as needed.
Ready to take your Excel reporting to the next level? Coefficient helps you automate date-based reports by connecting your spreadsheets directly to your business systems. Try Coefficient today to streamline your reporting workflow and ensure your data is always up-to-date. Get started with Coefficient

